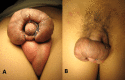
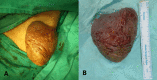
Penile Keloid Successfully Cured in a Keloid High-Tendency Patient
- PMID: 36741621
- PMCID: PMC9894642
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.33284
Penile Keloid Successfully Cured in a Keloid High-Tendency Patient
Abstract
Keloid scars are a relatively common condition but extremely rare in the penis. This case aims to be added to the previous 34 cases of penile keloid reported in the literature. We present the case of a 15-year-old patient with a high keloid-forming tendency who was successfully cured of penile keloid scarring with excision alone and without any adjuvant therapy. No recurrence was reported over eight years of follow-up. In contrast, at the same time, recurrence is frequently observed in other body parts after excision, making this particular part of the body an area of less keloid occurrence and recurrence.
Keywords: keloid; keloid scar; keloid therapy; keloid treatment; penile keloid.
Copyright © 2023, Abualjubain et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Literature review and case report of post-circumcision keloid management.Arab J Urol. 2019 Aug 7;17(4):314-317. doi: 10.1080/2090598X.2019.1651016. eCollection 2019. Arab J Urol. 2019. PMID: 31723449 Free PMC article.
-
Two patients with penile keloids: a review of the literature.Ann Plast Surg. 1997 Dec;39(6):662-5. doi: 10.1097/00000637-199712000-00022. Ann Plast Surg. 1997. PMID: 9418933
-
The Role of Plastic Surgery in the Treatment of Recurrent and Large Penile Keloid.Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022 Jan 26;10(1):e4052. doi: 10.1097/GOX.0000000000004052. eCollection 2022 Jan. Plast Reconstr Surg Glob Open. 2022. PMID: 35186620 Free PMC article.
-
A Retrospective Registry Study Evaluating the Long-Term Efficacy and Safety of Superficial Radiation Therapy Following Excision of Keloid Scars.J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020 Oct;13(10):12-16. Epub 2020 Oct 1. J Clin Aesthet Dermatol. 2020. PMID: 33584951 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Assessing keloid recurrence following surgical excision and radiation.Burns Trauma. 2020 Nov 14;8:tkaa031. doi: 10.1093/burnst/tkaa031. eCollection 2020. Burns Trauma. 2020. PMID: 33225004 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Post-circumcision keloid - a case report. Eldin US. http://www.medbc.com/annals/review/vol_12/num_3/text/vol12n3p174.htm Ann Burns Fire Disasters. 1999;12:174.
-
- Are prophylactic measures necessary to prevent recurrence of penile keloids? Abdelhalim A, Atwa AM, Soltan MA, Edwan M, Helmy TE, Hafez AT, Dawaba ME. Urology. 2020;141:147–149. - PubMed
-
- Keloids--clinical diagnosis, pathogenesis, and treatment options. Marneros AG, Krieg T. J Dtsch Dermatol Ges. 2004;2:905–913. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources