The Importance of Frontal QRS-T Angle in Predicting the Effectiveness and Success of Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients With Acute Pulmonary Embolism
- PMID: 36741663
- PMCID: PMC9891712
- DOI: 10.7759/cureus.33268
The Importance of Frontal QRS-T Angle in Predicting the Effectiveness and Success of Thrombolytic Therapy in Patients With Acute Pulmonary Embolism
Abstract
Objective: The frontal QRS-T angle (fQRS-T) is associated with myocardial ischemia and ventricular arrhythmias. On the other hand, acute pulmonary embolism (APE) is a major risk factor for cardiac adverse events. This research aimed to determine whether the fQRS-T, a marker of ventricular heterogeneity, can be used to predict successful thrombolytic therapy in patients with APE.
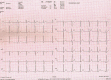
Methods: This was a retrospective observational study. Patients diagnosed with APE and hospitalized in the intensive care unit between 2020 and 2022 were included in the research. A total of 136 individuals with APEs were enrolled in this research. The patients were divided into two groups: thrombolytic-treated (n=64) and non-treated (moderate to severe risk, n=72). An ECG was conducted for each patient, and echocardiography was performed.
Results: The mean age of the thrombolytic group was 58.2±17.6 years, with 35 females (55.1% of the group) and 29 males (44.9%). The non-thrombolytic group had a mean age of 63.1±16.2, with 41 females (56.5%) and 31 males (43.5%). Respiratory rate, heart rate, and fQRS-T were higher in the thrombolytic group, and oxygen saturation ratio and systolic and diastolic blood pressure were higher in the non-thrombolytic group (p=0.006, p<0.001, p=0.021; p<0.001, p=0.015, p<0.001, respectively). In the thrombolytic therapy group, comparing pre- and post-treatment ECG data revealed a statistically significant change in the fQRS-T value (p=0.019).
Conclusion: The fQRS-T may provide important clues for the successful treatment of APEs.
Keywords: acute pulmonary embolism; echocardiography; frontal qrs-t angle; hemodynamic instability; thrombolysis.
Copyright © 2023, Durgun et al.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
-
- Modified model for end-stage liver disease score predicts 30-day mortality in high-risk patients with acute pulmonary embolism admitted to intensive care units. İdin K, Dereli S, Kaya A, Yenerçağ M, Yılmaz AS, Tayfur K, Gülcü O. Scand Cardiovasc J. 2021;55:237–244. - PubMed
-
- Global burden of thrombosis: epidemiologic aspects. Wendelboe AM, Raskob GE. Circ Res. 2016;118:1340–1347. - PubMed
-
- Kronik Obstrüktif Akciğer Hastalığı Ciddiyeti ile Sağ VentrikülStrain İlişkisi [Correlation of chronic obstructive pulmonary disease severity and right ventricular strain] Günlü S, Akkaya S, Polat C, Ede H, Öztur O. https://search.trdizin.gov.tr/yayin/detay/446195/ MN Kardiyol. 2021;28:74–79.
-
- Excitation-contraction coupling and relaxation alteration in right ventricular remodelling caused by pulmonary arterial hypertension. Antigny F, Mercier O, Humbert M, Sabourin J. Arch Cardiovasc Dis. 2020;113:70–84. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous