Changing trends of the disease burden of non-rheumatic valvular heart disease in China from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions: Findings from global burden of disease study
- PMID: 36741848
- PMCID: PMC9897059
- DOI: 10.3389/fcvm.2022.912661
Changing trends of the disease burden of non-rheumatic valvular heart disease in China from 1990 to 2019 and its predictions: Findings from global burden of disease study
Abstract
Objective: China has an increasing burden of non-rheumatic valvular heart disease (NRVHD) as the aging of the population is deepening. The aim was to assess the age and sex-specific prevalence and DALYs of NRVHD in China from 1990 to 2019 and to predict the burden in the next 25 years.
Methods: The Global Burden of Disease Study (2019) was used to extract the data of age- and sex-specific incidence, mortality, and disability-adjusted life years (DALYs) of NRVHD in China, 1990-2019. We estimated the annual percentage change (EAPC) to access the temporal trends of the disease burden of NRVHD. The R package called Nordpred was used to perform an age-period-cohort analysis to predict the prevalence of NRVHD in the next 25 years.
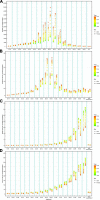
Results: The number of incident cases of NRVHD increased from 93.16 thousand in 1990 to 325.05 thousand in 2019. Overall upward trends were observed in the age-standardized incidence rate (ASIR) from 1990 to 2019. Significant temporal trends in mortality and DALYs of NRVHD were observed. High systolic blood pressure, high sodium diet, and lead exposure were the main driving forces for NRVHD. In the next 25 years, the number of new cases and deaths of NRVHD should continue to increase to 390.64 thousand and 10.0 thousand, respectively. The ASIR should show an upward trend, while the ASMR should show a downward trend among men and women.
Conclusion: In China, the overall rates of NRVHD have increased over the past 30 years, and there has been a substantial increase in the burden of NRVHD due to population growth and aging and will continue to increase in the next 25 years. Our results can help shape a multifactorial approach and public policy to reduce the NRVHD burden throughout China.
Keywords: disease burden; non-rheumatic valvular heart disease; prediction; risk factor; temporal trend.
Copyright © 2023 Zheng, Guan and Lin.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Liu F, Xue Y, Liao H, Zhan X, Guo H, Huang H, et al. Five-year epidemiological survey of valvular heart disease: changes in morbidity, etiological spectrum and management in a cardiovascular center of southern china. J Thorac Dis. (2014) 6:1724–30. 10.3978/j.issn.2072-1439.2014.11.21 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Marijon E, Celermajer D, Tafflet M, El-Haou S, Jani D, Ferreira B, et al. Rheumatic heart disease screening by echocardiography: the inadequacy of world health organization criteria for optimizing the diagnosis of subclinical disease. Circulation. (2009) 120:663–8. 10.1161/CIRCULATIONAHA.109.849190 - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous

