Real-time polymerase chain reaction methods for strain specific identification and enumeration of strain Lacticaseibacillus paracasei 8700:2
- PMID: 36741903
- PMCID: PMC9889646
- DOI: 10.3389/fmicb.2022.1076631
Real-time polymerase chain reaction methods for strain specific identification and enumeration of strain Lacticaseibacillus paracasei 8700:2
Abstract
Introduction: Reliable and accurate methods for probiotic identification and enumeration, at the strain level plays a major role in confirming product efficacy since probiotic health benefits are strain-specific and dose-dependent. In this study, real-time PCR methods were developed for strain specific identification and enumeration of L. paracasei 8700:2, a probiotic strain that plays a role in fighting the common cold.
Methods: The assay was designed to target a unique region in L. paracasei 8700:2 genome sequence to achieve strain level specificity. The identification assay was evaluated for specificity and sensitivity. The enumeration viability real-time PCR (v-qPCR) method was first optimized for the viability treatment, then the method was evaluated for efficiency, limit of quantification, precision, and its performance was compared to plate count (PC) and viability droplet digital PCR (v-ddPCR) methods.
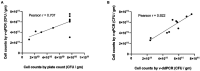
Results: The identification method proved to be strain specific and highly sensitive with a limit of detection of 0.5 pg of DNA. The optimal viability dye (PMAxx) concentration was 50 μM. The method was efficient (> 90% with R 2 values > 0.99), with a linear dynamic range between 6*102 and 6*105 copies. The method was highly precise with a relative standard deviation below 5%. The Pearson correlation coefficient (r) was 0.707 for PC and v-qPCR methods, and 0.922 for v-qPCR and v-ddPCR. Bland-Altman method comparison showed that v-qPCR always gave higher values compared to PC method (relative difference ranging from 119% to 184%) and showed no consistent trend (relative difference ranging from -20% to 22%) when comparing v-qPCR and v-ddPCR methods.
Discussion: The difference between PC and v-PCR methods can potentially be attributed to the proportion of cells that exist in a viable but non culturable (VBNC) state, which can be count by v-PCR but not with PC. The developed v-qPCR method was confirmed to be strain specific, sensitive, efficient, with low variance, able to count VBNC cells, and has shorter time to results compared to plate count methods. Thus, the identification and enumeration methods developed for L. paracasei 8700:2 will be of great importance to achieve high quality and efficacious probiotic products.
Keywords: Lactobacillus paracasei 8700:2; PMAxx; probe-based assay; probiotics; real-time PCR; strain specific PCR assay; viability PCR; viable but non-culturable.
Copyright © 2023 Shehata, Hassane and Newmaster.
Conflict of interest statement
HS and BH were employed by Purity-IQ Inc. The remaining author declares that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures






Similar articles
-
Real-time PCR methods for identification and stability monitoring of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum UABl-14 during shelf life.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 19;15:1360241. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1360241. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38706967 Free PMC article.
-
Enumeration of Probiotic Strain Lacticaseibacillus rhamnosus GG (ATCC 53103) Using Viability Real-time PCR.Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2021 Dec;13(6):1611-1620. doi: 10.1007/s12602-021-09849-6. Epub 2021 Sep 30. Probiotics Antimicrob Proteins. 2021. PMID: 34591288
-
Quantification of Lactobacillus paracasei viable cells in probiotic yoghurt by propidium monoazide combined with quantitative PCR.Int J Food Microbiol. 2018 Jan 2;264:1-7. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfoodmicro.2017.10.021. Epub 2017 Oct 18. Int J Food Microbiol. 2018. PMID: 29073460
-
Probiotic and postbiotic analytical methods: a perspective of available enumeration techniques.Front Microbiol. 2023 Dec 7;14:1304621. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1304621. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 38192285 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Enumeration of probiotic strains: Review of culture-dependent and alternative techniques to quantify viable bacteria.J Microbiol Methods. 2014 Aug;103:9-17. doi: 10.1016/j.mimet.2014.04.012. Epub 2014 May 9. J Microbiol Methods. 2014. PMID: 24814752 Review.
Cited by
-
Real-time PCR methods for identification and stability monitoring of Bifidobacterium longum subsp. longum UABl-14 during shelf life.Front Microbiol. 2024 Apr 19;15:1360241. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1360241. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38706967 Free PMC article.
-
Development and validation of a PMA-qPCR method for accurate quantification of viable Lacticaseibacillus paracasei in probiotics.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 7;15:1456274. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1456274. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39171269 Free PMC article.
-
The power of DNA based methods in probiotic authentication.Front Microbiol. 2023 Apr 17;14:1158440. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2023.1158440. eCollection 2023. Front Microbiol. 2023. PMID: 37138639 Free PMC article.
-
Viability-PCR for the selective detection of Lactobacillus acidophilus and Bifidobacterium bifidum in live bacteria-containing products.Front Microbiol. 2024 Jul 3;15:1400529. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1400529. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39021625 Free PMC article.
-
Bifidobacterium species viability in dairy-based probiotic foods: challenges and innovative approaches for accurate viability determination and monitoring of probiotic functionality.Front Microbiol. 2024 Feb 2;15:1327010. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1327010. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 38371928 Free PMC article. Review.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

