Alagille Syndrome and Repeat Oxygenator Failure during Cardiopulmonary Bypass: A Word of Caution
- PMID: 36742021
- PMCID: PMC9891473
- DOI: 10.1182/ject-2200022
Alagille Syndrome and Repeat Oxygenator Failure during Cardiopulmonary Bypass: A Word of Caution
Abstract
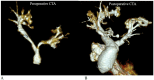
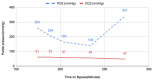
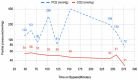
Alagille syndrome is an autosomal dominant disorder that is caused by heterozygous mutation of JAG1 or NOTCH2 gene that impacts several multisystem organs including but may not be limited to the liver, heart, musculoskeletal, skin, and the eyes. The most common congenital heart defect associated with Alagille syndrome is multilevel right ventricular outflow tract obstruction with multiple central and peripheral branch pulmonary arterial stenoses occurring in up to two-thirds of these patients. We report two cases of Alagille syndrome who underwent extensive pulmonary arterial branch rehabilitation and experienced unusual oxygenator failure during cardiopulmonary bypass (CPB). We present lessons learned from these two cases and the changes that we implemented in our practice that facilitated smooth conduct of CPB in other cases that we performed subsequently.
Keywords: Alagille syndrome; oxygenator failure.; pulmonary arterioplasty; pulmonary artery reconstruction.
© Copyright 2022 AMSECT.
Figures

References
-
- Mitchell E, Gilbert M, Loomes KM. Alagille syndrome. Clin Liver Dis. 2018;22:625–41. - PubMed
-
- Emerick KM, Rand EB, Goldmuntz E, et al. . Features of Alagille syndrome in 92 patients: Frequency and relation to prognosis. Hepatology 1999;29:822–9. - PubMed
-
- McElhinney DB, Krantz ID, Bason L, et al. . Analysis of cardiovascular phenotype and genotype-phenotype correlation in individuals with a JAG1 mutation and/or Alagille syndrome. Circulation 2002;106:2567–74. - PubMed
-
- Mainwaring RD, Sheikh AY, Punn R, et al. . Surgical outcomes for patients with pulmonary atresia/major aortopulmonary collaterals and Alagille syndrome. Eur J Cardiothorac Surg. 2012;42:235–41. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous
