Benefits of Huang Lian mediated by gut microbiota on HFD/STZ-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice
- PMID: 36742405
- PMCID: PMC9889990
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2023.1120221
Benefits of Huang Lian mediated by gut microbiota on HFD/STZ-induced type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice
Abstract
Background: Huang Lian (HL), one of the traditional Chinese medicines (TCMs) that contains multiple active components including berberine (BBR), has been used to treat symptoms associated with diabetes for thousands of years. Compared to the monomer of BBR, HL exerts a better glucose-lowering activity and plays different roles in regulating gut microbiota. However, it remains unclear what role the gut microbiota plays in the anti-diabetic activity of HL.
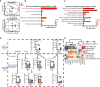
Methods: In this study, a type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM) mouse model was induced with a six-week high-fat diet (HFD) and a one-time injection of streptozotocin (STZ, 75 mg/kg). One group of these mice was administrated HL (50 mg/kg) through oral gavage two weeks after HFD feeding commenced and continued for four weeks; the other mice were given distilled water as disease control. Comprehensive analyses of physiological indices related to glycolipid metabolism, gut microbiota, untargeted metabolome, and hepatic genes expression, function prediction by PICRUSt2 were performed to identify potential mechanism.
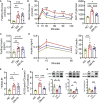
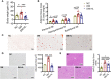
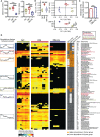
Results: We found that HL, in addition to decreasing body fat accumulation, effectively improved insulin resistance by stimulating the hepatic insulin-mediated signaling pathway. In comparison with the control group, HL treatment constructed a distinct gut microbiota and bile acid (BA) profile. The HL-treated microbiota was dominated by bacteria belonging to Bacteroides and the Clostridium innocuum group, which were associated with BA metabolism. Based on the correlation analysis, the altered BAs were closely correlated with the improvement of T2DM-related markers.
Conclusion: These results indicated that the anti-diabetic activity of HL was achieved, at least partly, by regulating the structure of the gut microbiota and the composition of BAs.
Keywords: Huang Lian; bile acids; gut microbiota; microbial BA metabolism; type 2 diabetes mellitus.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Feng, Li, Pan, Luo, Liu, Ding, Wang, Xu, Zhao and Zhang.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Jiang-Tang-San-Huang pill alleviates type 2 diabetes mellitus through modulating the gut microbiota and bile acids metabolism.Phytomedicine. 2023 May;113:154733. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2023.154733. Epub 2023 Feb 26. Phytomedicine. 2023. PMID: 36870307
-
Simiao Wan modulates the gut microbiota and bile acid metabolism during improving type 2 diabetes mellitus in mice.Phytomedicine. 2022 Sep;104:154264. doi: 10.1016/j.phymed.2022.154264. Epub 2022 Jun 13. Phytomedicine. 2022. PMID: 35752076
-
High Fat Diet and High Sucrose Intake Divergently Induce Dysregulation of Glucose Homeostasis through Distinct Gut Microbiota-Derived Bile Acid Metabolism in Mice.J Agric Food Chem. 2024 Jan 10;72(1):230-244. doi: 10.1021/acs.jafc.3c02909. Epub 2023 Dec 11. J Agric Food Chem. 2024. PMID: 38079533
-
Edible traditional Chinese medicines improve type 2 diabetes by modulating gut microbiotal metabolites.Acta Diabetol. 2024 Apr;61(4):393-411. doi: 10.1007/s00592-023-02217-6. Epub 2024 Jan 16. Acta Diabetol. 2024. PMID: 38227209 Review.
-
Type-2 Diabetes Mellitus and the Gut Microbiota: Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Nov 30;15(11):e49740. doi: 10.7759/cureus.49740. eCollection 2023 Nov. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38161953 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Effect of Gegen Qinlian Decoction on the regulation of gut microbiota and metabolites in type II diabetic rats.Front Microbiol. 2024 Aug 21;15:1429360. doi: 10.3389/fmicb.2024.1429360. eCollection 2024. Front Microbiol. 2024. PMID: 39234553 Free PMC article.
-
Causal effects of gut microbiota on diabetic neuropathy: a two-sample Mendelian randomization study.Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024 Aug 2;15:1388927. doi: 10.3389/fendo.2024.1388927. eCollection 2024. Front Endocrinol (Lausanne). 2024. PMID: 39157679 Free PMC article.
-
Updated Progress on Polysaccharides with Anti-Diabetic Effects through the Regulation of Gut Microbiota: Sources, Mechanisms, and Structure-Activity Relationships.Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024 Apr 2;17(4):456. doi: 10.3390/ph17040456. Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2024. PMID: 38675416 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Managing Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus via the Regulation of Gut Microbiota: A Chinese Medicine Perspective.Nutrients. 2024 Nov 18;16(22):3935. doi: 10.3390/nu16223935. Nutrients. 2024. PMID: 39599721 Free PMC article. Review.
-
AGDMP1 alleviates insulin resistance by modulating heat shock protein 60-mediated IRS-1/AKT/GLUT4 pathway and adipose inflammation: A potential therapeutic peptide for gestational diabetes mellitus.FASEB J. 2025 Jan 31;39(2):e70339. doi: 10.1096/fj.202402886R. FASEB J. 2025. PMID: 39854096 Free PMC article.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

