Evaluation of Thyroid Nodule: Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS) and Clinicopathological Correlation
- PMID: 36742631
- PMCID: PMC9895183
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-021-02461-8
Evaluation of Thyroid Nodule: Thyroid Imaging Reporting and Data System (TIRADS) and Clinicopathological Correlation
Abstract
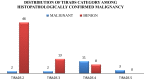
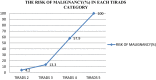
Ultrasound is one of the accepted modality for the initial assessment of thyroid nodules. Thyroid image reporting and data system (TIRADS) classification system is the most useful of the risk stratification systems of thyroid imaging in predicting malignancy. The purpose of this study is to assess the clinical usefulness of TIRADS in the evaluation of thyroid nodule and compare it with final histopathological results. This was a prospective observational study conducted in a tertiary care hospital over a period of one year. Preoperative ultrasound was performed in 85 patients admitted for thyroid surgery. Thyroid nodules were classified according to TIRADS into five groups. The TIRADS category was compared with the final histopathological diagnosis following surgery. Sensitivity, specificity, positive as well as negative predictive value and risk of malignancy for each TIRADS category was assessed. The risk of malignancy for TIRADS 2, TIRADS 3, TIRADS 4, and TIRADS 5 was 4.2%, 13.3%, 57.9% and 100%, respectively. The usefulness of TIRADS classification in prediction of malignancy was 77.8% sensitive, 89.6% specific, had a positive predictive value of 66.6% and negative predictive value of 93.8%. The probability of a particular nodule being malignant can be inferred from ultrasound based TIRADS system. Hence ACR TIRADS classification is a valuable tool for diagnosis of thyroid nodule and should be adopted in our routine clinical practice.
Keywords: Histopathological correlation; Thyroid imaging reporting and data system (TIRADS); Thyroid nodule; Ultrasonography.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2021.
Figures
References
-
- Usha Menon V, Sundaram KR, Unnikrishnan AG, Jayakumar RV, Nair V, Kumar H. High prevalence of undetected thyroid disorders in an iodine sufficient adult south Indian population. J Indian Med Assoc. 2009;107(2):72–77. - PubMed
-
- Lauria Pantano A, Maddaloni E, Briganti SI, Beretta Anguissola G, Perrella E, Taffon C, Palermo A, Pozzilli P, Manfrini S, Crescenzi A. Differences between ATA, AACE/ACE/AME and ACR TI-RADS ultrasound classifications performance in identifying cytological high-risk thyroid nodules. Eur J Endocrinol. 2018;178(6):595–603. doi: 10.1530/EJE-18-0083. - DOI - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources