Coblation Versus Cold Dissection Tonsillectomy: A Comparative Study
- PMID: 36742713
- PMCID: PMC9895176
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-022-03079-0
Coblation Versus Cold Dissection Tonsillectomy: A Comparative Study
Abstract
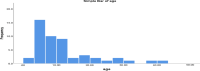
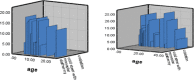
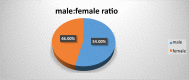
Tonsillectomy is the most frequently performed surgery in the recent years. Many techniques have been advocated to improve surgical efficacy and decrease postoperative morbidity. Probably the most update was coblation tonsillectomy. This is a comparative study which was conducted on 50 patients (23 females and 27 males) who underwent tonsillectomy operations, 25 patients using cold steel dissection method whereas coblation technique was used for the rest 25 patients. Follow up was done at day 1, 3, 7 and 14 and the related parameters were calculated. The mean age of patients was 11.6 years with a mean of 2.2-40 years. There were 27 (54%) males out of 50 and 23 (46%) were females. Male to female ratio was 54%:46% ≈ 1.17:1. The current study revealed significant difference between coblation versus cold dissection tonsillectomy. Postoperative pain was significantly less at day 3 and day 7 using coblation technique. Moreover, there were less intraoperative bleeding, less time in days to return to normal diet and less time to return to normal activities. We believe that coblation tonsillectomy carries less morbidity than cold steel dissection, hence we recommend it to be applied at our hospital.
Keywords: Coblation; Cold steel dissection method; Tonsillectomy.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2022.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestAll authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures



Similar articles
-
Comparison of Clinical and Functional Outcome of Cold Steel Dissection versus Coblation Technique in Tonsillectomy.J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2022 Mar 13;19(4):820-823. doi: 10.33314/jnhrc.v19i04.3961. J Nepal Health Res Counc. 2022. PMID: 35615844
-
Coblation tonsillectomy: is it inherently bloody?Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012 Feb;269(2):579-83. doi: 10.1007/s00405-011-1609-8. Epub 2011 May 6. Eur Arch Otorhinolaryngol. 2012. PMID: 21547390
-
A pilot randomized controlled trial of coblation tonsillectomy versus dissection tonsillectomy with bipolar diathermy haemostasis.Clin Otolaryngol. 2007 Aug;32(4):261-7. doi: 10.1111/j.1365-2273.2007.01468.x. Clin Otolaryngol. 2007. PMID: 17651267 Clinical Trial.
-
Coblation versus cold dissection in paediatric tonsillectomy: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Laryngol Otol. 2020 Mar;134(3):197-204. doi: 10.1017/S0022215120000377. Epub 2020 Mar 2. J Laryngol Otol. 2020. PMID: 32114992
-
Tonsillectomy Outcomes for Coblation Versus Bipolar Diathermy Techniques in Adult Patients: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Ear Nose Throat J. 2023 Apr;102(4):NP183-NP191. doi: 10.1177/0145561321994995. Epub 2021 Mar 15. Ear Nose Throat J. 2023. PMID: 33719616
References
-
- Friedman M, Schalch P (2009) Radiofrequency tonsil reduction: safety, morbidity and efficacy. In: Sleep apnea and snoring. Elsevier, pp 429–33 - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
