"Association of High Risk Factors and Hearing Impairment in Infants-A Hospital Based Study"
- PMID: 36742726
- PMCID: PMC9895604
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-021-02760-0
"Association of High Risk Factors and Hearing Impairment in Infants-A Hospital Based Study"
Abstract
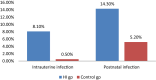
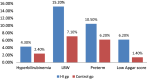
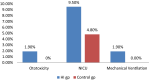
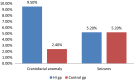
The aim of the study was to find the association of various risk factors with permanent hearing impairment in infants. A case-control study was designed on 420 infants with permanent hearing impairment and normal hearing. The case control ratio was 1:1. Alternate sampling method was used for selecting the control group. Review of medical records and parent interview was done to collect the information of risk factors. Family history(adj. OR 7.5; 95% CI 3, 14; P = 0.000), Consanguinity (adj. OR: 4; 95% CI 2,4; P = 0.000), intra uterine infection (adj. OR 18, 95% CI: 2.3-126.5, P = 0.000), post natal infection (adj. OR 3, 95% CI: 1.3-5, P = 0.004), low Apgar score (adj.OR: 4.6, 95% CI: 1.3-15), craniofacial anomaly (OR-4.6, 95% CI: 1.4-9.5, P = 0.005) and low birth weight (adj. OR: 2.3, 95% CI: 1.2-3.8) were significantly associated with hearing impairment. Among the risk factors, intra uterine infection was having highest significant association with permanent hearing impairment. This is followed by family history, low Apgar score, craniofacial anomaly, consanguinity, post natal infection and low birth weight.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2021.
Figures
References
-
- ICMR, Collaborative study on prevalence and aetiology of hearing impairment. Project report., New Delhi, 1983.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources