Infection Control and Hygienic Measures Practiced Among Audiologists in India
- PMID: 36742729
- PMCID: PMC9895510
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-020-01799-9
Infection Control and Hygienic Measures Practiced Among Audiologists in India
Abstract
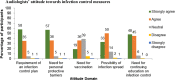
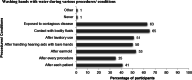
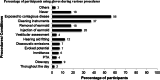
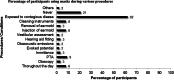
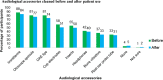
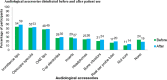
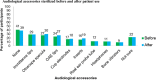
Audiologists extend their services to wide range of patients who vary across several factors like age, disease, nutritional status, pharmacological intervention, socioeconomic status and compromised immune systems. This involves direct or indirect contact with patients exposing the clinician to blood, and other bodily fluids which are considered to be potentially infectious substances. Thus infection control activities must be stressed with the goal of reducing or preventing the transmission of nosocomial pathogens to patients and staff. The aim of the study is to provide an in-depth assessment of current infection control strategies and hygienic measures followed among Audiologists in India. An internet based questionnaire survey was done among 172 Audiologists. The questionnaire focused on four domains: demography; knowledge, attitude and practice of infection control and hygienic measures followed in audiology clinic. Majority of the participants had a positive attitude towards infection control practice. Though most of them had an access to gloves (73.3%) and masks (60%), their usage was minimal and restricted to selected procedures. Hand hygienic measures were practiced by 89% of the participants only during few procedures. Irrespective of critical or non-critical instruments, majority of the participants preferred cleaning and disinfecting. Sterilisation of critical instruments was performed only by 30% of the audiologists. Audiologists knowledge and practice of infection control and hygienic measures was found to be inadequate. Specialized training program on infection control strategies should be targeted to the newly graduated and practicing audiologists to ensure patient safety and infection free clinical environment.
Keywords: Audiologist; Disinfection; Hand hygiene; Infection control; Sterilisation.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2020.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThere is no conflict of interest.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Infection prevention and control measures in audiology practice within public healthcare facilities in KwaZulu-Natal province, South Africa.S Afr J Commun Disord. 2019 Dec 2;66(1):e1-e14. doi: 10.4102/sajcd.v66i1.636. S Afr J Commun Disord. 2019. PMID: 31793311 Free PMC article.
-
Tele-Audiology in India: Current and Future Trends in Knowledge, Attitude, and Practice Among Audiologists.J Audiol Otol. 2022 Jul;26(3):130-141. doi: 10.7874/jao.2021.00584. Epub 2022 May 12. J Audiol Otol. 2022. PMID: 35538867 Free PMC article.
-
Audiological practice in India: an internet-based survey of audiologists.Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013 Dec;65(Suppl 3):636-44. doi: 10.1007/s12070-013-0674-2. Epub 2013 Aug 2. Indian J Otolaryngol Head Neck Surg. 2013. PMID: 24427729 Free PMC article.
-
Professional Guidelines and Reported Practice of Audiologists Performing Fall Risk Assessment With Older Adults: A Systematic Review.Am J Audiol. 2022 Mar 3;31(1):243-260. doi: 10.1044/2021_AJA-21-00148. Epub 2022 Feb 11. Am J Audiol. 2022. PMID: 35148482
-
[Procedures for hand hygiene in German-speaking countries].Zentralbl Hyg Umweltmed. 1996 Dec;199(2-4):334-49. Zentralbl Hyg Umweltmed. 1996. PMID: 9409922 Review. German.
References
-
- World Health Organization (2019) Infection prevention and control (Internet). https://www.who.int/gpsc/ipc/en. Cited 24 Sep 2019
-
- Kemp RJ, Bankaitis AU (2000) Infection control in audiology. Audiology online [Internet]. http://www.audiologyonline.com/articles/infection-control-in-audiology-1299. Cited 9 Apr 2018
-
- The Canadian Interorganizational Group for Speech Language Pathology and Audiology (2000) Infection prevention and control guidelines for audiology [Internet]. https://canadianaudiology.ca/wp-content/uploads/2016/11/Infection-Preven.... Cited 9 Apr 2018
-
- Kemp RJ, Roeser RJ. Infection control for audiologists. Semin Hear. 1998;19(2):195–204. doi: 10.1055/s-0028-1082968. - DOI
-
- Katz J, Chasin M, English K, Hood LJ, Tillery KL, editors. Handbook of clinical audiology. 7. Philadelphia: Wolters Kluwer Health; 2015.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
