Supraglottic Schwannoma: Dilemma and Challenges in Management
- PMID: 36742766
- PMCID: PMC9895650
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-021-03027-4
Supraglottic Schwannoma: Dilemma and Challenges in Management
Abstract
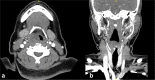
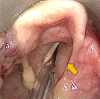
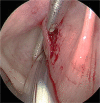
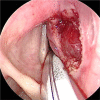
Laryngeal schwannomas are rare lesions that represent less than 1.5% of all benign laryngeal tumors. Its slow and submucosal growth may cause a delay in consultation and management. Herein, a case of right supraglottic schwannoma is diagnosed in a 34-year-old lady who was unconcerned about hoarseness for 10 years. She was referred to otorhinolaryngology clinic for assessment when hoarseness was detected during consultation for a gynecology surgery. Apart from hoarseness, there were no noisy breathing, shortness of breath or aspiration symptoms. Flexible nasopharyngolaryngoscopy showed a submucosal bulge at the right vestibular fold obscuring the vocal fold causing an airway concern. Computer tomography scan of the neck revealed a heterogenous enhancing mass centered at the right supraglottis measuring 2.6 × 2.7 × 2.7 cm. There were no erosions of the adjacent thyroid and arytenoid cartilages. Subsequently, complete excision of the lesion was done endoscopically. Definitive diagnosis of schwannoma was obtained via histopathology examination. This paper presents our approach and operative steps in the excision of this lesion using microlaryngoscopy with cold instruments.
Keywords: Larynx; Schwannoma; Supraglottic; Tumor.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflicts of interestNone.
Figures




Similar articles
-
Laryngeal Schwannoma, Alarming Mass of Airway: A Case Report.JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2021 Nov 15;59(243):1185-1188. doi: 10.31729/jnma.6345. JNMA J Nepal Med Assoc. 2021. PMID: 35199768 Free PMC article.
-
Laryngeal schwannoma treated with a CO2 laser: A case report.Oncol Lett. 2015 Mar;9(3):1467-1469. doi: 10.3892/ol.2015.2858. Epub 2015 Jan 8. Oncol Lett. 2015. PMID: 25663932 Free PMC article.
-
Challenges in managing a vagal schwannomas: Lesson learnt.Int J Surg Case Rep. 2018;53:5-8. doi: 10.1016/j.ijscr.2018.10.025. Epub 2018 Oct 19. Int J Surg Case Rep. 2018. PMID: 30366175 Free PMC article.
-
Laryngeal paraganglioma: an updated critical review.Acta Otolaryngol. 2004 Nov;124(9):995-9. doi: 10.1080/00016480410017576. Acta Otolaryngol. 2004. PMID: 15513540 Review.
-
Preservation of laryngeal function through reconstruction of the supraglottis and thyrohyoid membrane with a chimeric anterolateral thigh flap after supraglottic laryngectomy: A case report and literature review.Microsurgery. 2021 Jul;41(5):462-467. doi: 10.1002/micr.30708. Epub 2021 Jan 18. Microsurgery. 2021. PMID: 33462924 Review.
Cited by
-
Transoral Endoscopic-Assisted Resection of Laryngeal Schwannoma: A Case Report.Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2024 Jan;36(1):371-375. doi: 10.22038/IJORL.2023.71324.3427. Iran J Otorhinolaryngol. 2024. PMID: 38259691 Free PMC article.
References
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
