An Uncommon Differential for Mass in the Middle Ear Cleft-Temporal Meningoencephalocele
- PMID: 36742828
- PMCID: PMC9895547
- DOI: 10.1007/s12070-021-02983-1
An Uncommon Differential for Mass in the Middle Ear Cleft-Temporal Meningoencephalocele
Abstract
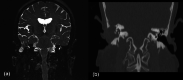
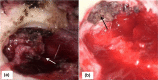
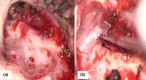
Meningoencephalocoele (ME) of the temporal bone is otherwise known as brain fungus. It is a rare and potentially life-threatening condition. It occurs in cases of chronic otitis media either as a complication or iatrogenically induced following mastoid surgeries. It requires prompt surgical intervention. High-resolution Computer tomography of Temporal bone and Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain are needed to detect these cases. Surgery can be otological, neurosurgical, or combined. We discuss a case of Iatrogenic Temporal meningoencephalocele and its management along with a review of the literature.
Keywords: CSF otorrhea; Chronic otitis media; Mastoid surgery; Meningoencephalocoele.
© Association of Otolaryngologists of India 2021.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestThe authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Gluckman J. Fungus cerebri-an unusual complication of mastoidectomy. S Afr Med J. 1975;49(46):1933–1934. - PubMed
-
- Kizilay A, Aladağ İ, Çokkeser Y, Ozturan O. Dural bone defects and encephalocele associated with chronic otitis media or its surgery. Kulak burun bogaz ihtisas dergisi: KBB= J Ear, Nose, Throat. 2002;9(6):403–409. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
