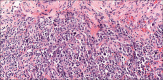
Suspicious perianal nodule
- PMID: 36743118
- PMCID: PMC9891017
- DOI: 10.4103/ijstd.ijstd_115_21
Suspicious perianal nodule
Conflict of interest statement
There are no conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Sukswai N, Lyapichev K, Khoury JD, Medeiros LJ. Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma variants: An update. Pathology. 2020;52:53–67. - PubMed
-
- Harmon CM, Smith LB. Plasmablastic lymphoma: A review of clinicopathologic features and differential diagnosis. Arch Pathol Lab Med. 2016;140:1074–8. - PubMed
-
- Makady NF, Ramzy D, Ghaly R, Abdel-Malek RR, Shohdy KS. The emerging treatment options of plasmablastic lymphoma: Analysis of 173 individual patient outcomes. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk Mar. 21(3):e255–e263. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources