Severe persistent mycobacteria antigen stimulation causes lymphopenia through impairing hematopoiesis
- PMID: 36743311
- PMCID: PMC9889370
- DOI: 10.3389/fcimb.2023.1079774
Severe persistent mycobacteria antigen stimulation causes lymphopenia through impairing hematopoiesis
Abstract
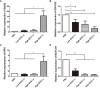
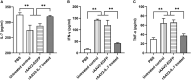
Miliary tubersculosis (TB), an acute systemic blood disseminated tuberculosis mainly caused by Mycobacterium tuberculosis (M. tuberculosis), can cause signs of lymphopenia in clinical patients. To investigate whether/how persistent mycobacteria antigen stimulation impairs hematopoiesis and the therapeutic effect of interleukin-7 (IL-7), a mouse model of Mycobacterium Bovis Bacillus Calmette-Guérin (BCG) intravenous infection with/without an additional stimulation with M. tuberculosis multi-antigen cocktail containing ESAT6-CFP10 (EC) and Mtb10.4-HspX (MH) was established. Consistent with what happened in miliary TB, high dose of BCG intravenous infection with/without additional antigen stimulation caused lymphopenia in peripheral blood. In which, the levels of cytokines IFN-γ and TNF-α in serum increased, and consequently the expression levels of transcription factors Batf2 and IRF8 involved in myeloid differentiation were up-regulated, while the expression levels of transcription factors GATA2 and NOTCH1 involved in lymphoid commitment were down-regulated, and the proliferating activity of bone marrow (BM) lineage- c-Kit+ (LK) cells decreased. Furthermore, recombinant Adeno-Associated Virus 2-mediated IL-7 (rAAV2-IL-7) treatment could significantly promote the elevation of BM lymphoid progenitors. It suggests that persistent mycobacteria antigen stimulation impaired lymphopoiesis of BM hematopoiesis, which could be restored by complement of IL-7.
Keywords: BCG; IL-7; hematopoiesis; lymphopenia; miliary tuberculosis; mycobacterium tuberculosis.
Copyright © 2023 Li, Ma, Li, Zhang, Han, Tan, Mi, Yang, Wang and Zhu.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Cordeiro Gomes A., Hara T., Lim V. Y., Herndler-Brandstetter D., Nevius E., Sugiyama T., et al. (2016). Hematopoietic stem cell niches produce lineage-instructive signals to control multipotent progenitor differentiation. Immunity 45 (6), 1219–1231. doi: 10.1016/j.immuni.2016.11.004 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

