Milk as a Non-Invasive and Alternative Sample for Serum in the Diagnosis of Animal Toxoplasmosis: A Systematic Review
- PMID: 36743359
- PMCID: PMC9884371
- DOI: 10.18502/ijph.v51i9.10551
Milk as a Non-Invasive and Alternative Sample for Serum in the Diagnosis of Animal Toxoplasmosis: A Systematic Review
Abstract
Background: Toxoplasmosis is one of the most important zoonotic parasitic diseases worldwide with a high impact on human and animal health. Body fluids such as milk are used to diagnose many parasitic diseases, including toxoplasmosis. Therefore, this study aimed to investigate the role of milk as a non-invasive and alternative sample for serum in the diagnosis of animal toxoplasmosis.
Methods: Five English-language databases (ScienceDirect, PubMed, ProQuest, Scopus, and Web of Science) were explored for published articles before Dec 2020.
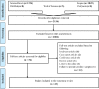
Results: In total, 42 out of 2256 published articles were included in this systematic review. In 21 articles, serum and milk samples were evaluated simultaneously with serological or molecular tests, and the results were compared. The results of descriptive studies and a review of nine experimental studies showed that milk could be used as a non-invasive and alternative sample for the serum in the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis.
Conclusion: Due to the relatively high prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii (T. gondii) infection in milk, consumption of raw milk from infected animals can be a potential source of human infection and a significant threat to public health. On the other hand, due to the ease and cheapness of collecting milk samples, the use of milk is recommended for the diagnosis of toxoplasmosis.
Keywords: Milk; Molecular; Non-invasive samples; Serological; Toxoplasma gondii.
Copyright © 2022 Nayeri et al. Published by Tehran University of Medical Sciences.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Unpasteurised milk consumption as a potential risk factor for toxoplasmosis in females with recurrent pregnancy loss.J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020 Nov;40(8):1106-1110. doi: 10.1080/01443615.2019.1702630. Epub 2020 Feb 4. J Obstet Gynaecol. 2020. PMID: 32013639
-
Toxoplasma gondii in naturally infected goats: Monitoring of specific IgG levels in serum and milk during lactation and parasitic DNA detection in milk.Prev Vet Med. 2019 Oct 1;170:104738. doi: 10.1016/j.prevetmed.2019.104738. Epub 2019 Jul 15. Prev Vet Med. 2019. PMID: 31421505
-
Saliva and tear as useful tools for the diagnosis of Toxoplasma gondii in human specimens: a systematic review.Ann Parasitol. 2022;68(2):201-213. doi: 10.17420/ap6802.426. Ann Parasitol. 2022. PMID: 35809338
-
Toxoplasmosis impact on prematurity and low birth weight.PLoS One. 2022 Jan 13;17(1):e0262593. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0262593. eCollection 2022. PLoS One. 2022. PMID: 35025961 Free PMC article.
-
[Problems and limitations of conventional and innovative methods for the diagnosis of Toxoplasmosis in humans and animals].Parassitologia. 2004 Jun;46(1-2):177-81. Parassitologia. 2004. PMID: 15305712 Review. Italian.
References
-
- Ouchetati I, Ouchene N, Khelifi-Ouchene NA, et al. (2020). Prevalence of Toxoplasma gondii infection among animals in Algeria: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Comp Immunol Microbiol Infect Dis, 101603. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials