Conventional and new-breeding technologies for improving disease resistance in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik)
- PMID: 36743558
- PMCID: PMC9896981
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1001682
Conventional and new-breeding technologies for improving disease resistance in lentil (Lens culinaris Medik)
Abstract
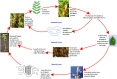
Lentil, an important cool season food legume, is a rich source of easily digestible protein, folic acid, bio-available iron, and zinc nutrients. Lentil grows mainly as a sole crop in the winter after harvesting rice in South Asia. However, the annual productivity is low due to its slow growth during the early phase, competitive weed infestation, and disease outbreaks during the crop growth period. Disease resistance breeding has been practiced for a long time to enhance resistance to various diseases. Often the sources of resistance are available in wild crop relatives. Thus, wide hybridization and the ovule rescue technique have helped to introgress the resistance trait into cultivated lentils. Besides hybridization, induced mutagenesis contributed immensely in creating variability for disease tolerance, and several disease-resistant mutant lines have been developed. However, to overcome the limitations of traditional breeding approaches, advancement in molecular marker technologies, and genomics has helped to develop disease-resistant and climate-resilient lentil varieties with more precision and efficiency. This review describes types of diseases, disease screening methods, the role of conventional and new breeding technologies in alleviating disease-incurred damage and progress toward making lentil varieties more resilient to disease outbreaks under the shadow of climate change.
Keywords: biotic stress; conventional breeding; disease outbreaks; lentil; new breeding technologies; yield.
Copyright © 2023 Roy, Sahu, Das, Bhattacharyya, Raina and Mondal.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
The Prospects of gene introgression from crop wild relatives into cultivated lentil for climate change mitigation.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 10;14:1127239. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1127239. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36998696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lentil adaptation to drought stress: response, tolerance, and breeding approaches.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Aug 20;15:1403922. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1403922. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39228838 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Chemical mutagenesis: role in breeding and biofortification of lentil (Lens culinaris Medik) mutant lines.Mol Biol Rep. 2022 Dec;49(12):11313-11325. doi: 10.1007/s11033-022-07678-6. Epub 2022 Jul 28. Mol Biol Rep. 2022. PMID: 35902448
-
Protein Biofortification in Lentils (Lens culinaris Medik.) Toward Human Health.Front Plant Sci. 2022 Apr 5;13:869713. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2022.869713. eCollection 2022. Front Plant Sci. 2022. PMID: 35449893 Free PMC article.
-
Molecular Breeding for Ascochyta Blight Resistance in Lentil: Current Progress and Future Directions.Front Plant Sci. 2017 Jun 29;8:1136. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2017.01136. eCollection 2017. Front Plant Sci. 2017. PMID: 28706526 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
The Prospects of gene introgression from crop wild relatives into cultivated lentil for climate change mitigation.Front Plant Sci. 2023 Mar 10;14:1127239. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2023.1127239. eCollection 2023. Front Plant Sci. 2023. PMID: 36998696 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Lentil adaptation to drought stress: response, tolerance, and breeding approaches.Front Plant Sci. 2024 Aug 20;15:1403922. doi: 10.3389/fpls.2024.1403922. eCollection 2024. Front Plant Sci. 2024. PMID: 39228838 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Adhikari A. D., Nielsen K. A., Harveson R. M., Graham C., Beck R., Mathew F. M. (2018). Bacterial blight of lentil (Lens culinaris) caused by pseudomonas syringae pv. syringae. Plant Health Progress. 19, 54–55. doi: 10.1094/PHP-11-17-0073-BR - DOI
-
- Aftab M., Iqbal S. M., Rauf C. A. (1992). Effect of lentil strain of pea seed-borne mosaic virus on lentil. Lentil Experim. News Service 19, 51–53.
-
- Ahmed A. U., Akhond M. A. Y. (2015). First report of sclerotinia rot caused by sclerotinia sclerotiorum in lens culinaris in Bangladesh. New Dis. Rep. 31, 23. doi: 10.5197/j.2044-0588.2015.031.023 - DOI
-
- Ahmed S., Morrall R. A. A. (1996). Field reactions of lentil lines and cultivars to isolates of ascochyta fabae f. sp. lentis. Can. J. Plant Pathol. 18, 362–369. doi: 10.1080/07060669609500589 - DOI
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources