Identification of PLATZ genes in Malus and expression characteristics of MdPLATZs in response to drought and ABA stresses
- PMID: 36743567
- PMCID: PMC9890193
- DOI: 10.3389/fpls.2022.1109784
Identification of PLATZ genes in Malus and expression characteristics of MdPLATZs in response to drought and ABA stresses
Abstract
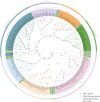
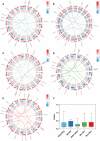
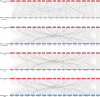
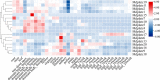
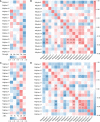
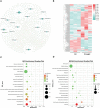
Plant AT-rich sequences and zinc-binding proteins (PLATZ) play crucial roles in response to environmental stresses. Nevertheless, PLATZ gene family has not been systemically studied in Rosaceae species, such as in apple, pear, peach, or strawberry. In this study, a total of 134 PLATZ proteins were identified from nine Rosaceae genomes and were classified into seven phylogenetic groups. Subsequently, the chromosomal localization, duplication, and collinearity relationship for apple PLATZ genes were investigated, and segmental duplication is a major driving-force in the expansion of PLATZ in Malus. Expression profiles analysis showed that PLATZs had distinct expression patterns in different tissues, and multiple genes were significantly changed after drought and ABA treatments. Furthermore, the co-expression network combined with RNA-seq data showed that PLATZ might be involved in drought stress by regulating ABA signaling pathway. In summary, this study is the first in-depth and systematic identification of PLATZ gene family in Rosaceae species, especially for apple, and provided specific PLATZ gene resource for further functional research in response to abiotic stress.
Keywords: Malus; PLATZ; Rosaceae species; co-expression network; drought stress.
Copyright © 2023 Sun, Liu, Liang, Luo, Yang, Feng, Wang, Guo, Ma and Zhao.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Azim J., Khan M., Hassan L., Robin A. (2020). Genome-wide characterization and expression profiling of plant-specific PLATZ transcription factor family genes in Brassica rapa l. Plant Breed. Biotechnol. 8 (1), 28–45. doi: 10.9787/PBB.2020.8.1.28 - DOI
-
- Bastian M., Heymann S., Jacomy M. (2009). Gephi: an open source software for exploring and manipulating networks. Int. AAAI Conf. weblogs Soc. media 8, 361–362. doi: 10.13140/2.1.1341.1520 - DOI
-
- Bhargava S., Sawant K. (2013). Drought stress adaptation: metabolic adjustment and regulation of gene expression. Plant Breed. 132 (1), 21–32. doi: 10.1111/pbr.12004 - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

