The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on a Greek cohort of patients with epilepsy
- PMID: 36743863
- PMCID: PMC9894308
The impact of the Covid-19 pandemic on a Greek cohort of patients with epilepsy
Abstract
Background: The Covid-19 pandemic, the subsequent lockdown, and the measures of social distancing may have had adverse effects on patients with epilepsy (PWE). This study was designed to assess the pandemic's psychological impact on the Greek non-infected PWE and possible changes in their seizure control.
Method: The patients were evaluated utilizing a semi-structured interview consisting of open questions regarding their demographic, social, and clinical characteristics, followed by five questions (on a scale of 0-10) related to the Covid-19 pandemic, lockdown, and social distancing measures. Anxiety and depression of PWE were screened using the Hospital Anxiety and Depression Scale (HADS), which consists of HADS-Anxiety and HADS-Depression subscales.
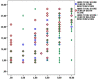
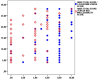
Results: We evaluated 65 PWE in the outpatient clinic (60 %) or via telephone interview (40 %). None of these patients experienced changes in seizure control. The mean scores of the Covid-19-related questions were 6.1 ± 2.7 (fear of getting infected), 4.7 ± 3.3 (fear of death), 7.1 ± 2.7 (fear of sickness for their relatives), 6.4 ± 3.1 (stress during lockdown), and 3.0 ± 2.9 (fear of antiepileptic drugs unavailability). Thirty-nine (60 %) patients screened positive for anxiety and thirty-three (50.8 %) for depression.
Conclusion: The psychological impact of the Covid-19 pandemic, lockdown, and social distancing measures on non-infected PWE was moderate without changes in their seizure control. HIPPOKRATIA 2021, 25 (4):145-150.
Keywords: Covid-19; Epilepsy; anxiety; depression; lockdown; psychological impact.
Copyright 2021, Hippokratio General Hospital of Thessaloniki.
Figures
References
-
- World Health Organization. The impact of COVID-19 on global health goals. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/spotlight/the-impact-of-covid-19-on-global.... date accessed: 09/01/2021.
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
