Effect of nocturnal hypoxemia on glycemic control among diabetic Saudi patients presenting with obstructive sleep apnea
- PMID: 36743921
- PMCID: PMC9889975
- DOI: 10.3389/fendo.2022.1020617
Effect of nocturnal hypoxemia on glycemic control among diabetic Saudi patients presenting with obstructive sleep apnea
Abstract
Background: Obstructive sleep apnea (OSA) is a prevalent disease that is associated with an increased incidence of type II diabetes mellitus (DM) if left untreated. We aimed to determine the association between glycosylated hemoglobin (HbA1c) levels and both nocturnal hypoxemia and apnea-hypopnea index (AHI) among a Saudi patients with OSA.
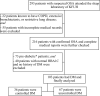
Methods: A cross-sectional study that enrolled 103 adult patients diagnosed with DM and confirmed to have OSA by full night attended polysomnography between 2018 and 2021. Those who presented with acute illness, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD)/restrictive lung diseases causing sleep-related hypoxemia, or no available HbA1c level within 6 months before polysomnography were excluded from the study. Univariate and multivariate linear regression analyses between HbA1c levels and parameters of interest were tested.
Results: Sixty-seven (65%) of the studied population had uncontrolled DM (HbA1c ≥7%). In univariate regression analysis, there was a significant positive association between HbA1c, and sleep time spent with an oxygen saturation below 90% (T90), female gender, and body mass index (BMI) (p<0.05) but not AHI, or associated comorbidities (p>0.05). In the multivariate analysis, HbA1c was positively associated with increasing T90 (p<0.05), and ODI (p<0.05), but not with AHI (p>0.05).
Conclusion: Nocturnal hypoxemia could be an important factor affecting glycemic control in patients with OSA suffering from DM irrespective of the severity of both diseases.
Keywords: T90; apnea/hypopnea index; glycosylated hemoglobin; hypoxia; nocturnal hypoxemia; obstructive sleep apnea.
Copyright © 2023 Mahmoud, Alotaibi, Almusally, Shafiek, Elamin, Alhaj, AlBaker, Elfaki, Qutub, Albahrani, Alabdrabalnabi, Al Saeed, Al Argan, Al.Rubaish, Alqurashi, Jatoi, Alharmaly, Almubarak, Al Said and Albahrani.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Similar articles
-
Association between severity of obstructive sleep apnea and glycated hemoglobin level in Japanese individuals with and without diabetes.Endocr J. 2018 Jan 30;65(1):121-127. doi: 10.1507/endocrj.EJ17-0356. Epub 2017 Sep 20. Endocr J. 2018. PMID: 28931780
-
Association of obstructive sleep apnea and nocturnal hypoxemia with all-cancer incidence and mortality: a systematic review and meta-analysis.J Clin Sleep Med. 2022 May 1;18(5):1427-1440. doi: 10.5664/jcsm.9772. J Clin Sleep Med. 2022. PMID: 34755597 Free PMC article.
-
Association of Diabetic Microvascular Complications and Parameters of Obstructive Sleep Apnea in Patients with Type 2 Diabetes.Diabetes Technol Ther. 2016 Jul;18(7):415-20. doi: 10.1089/dia.2015.0433. Epub 2016 Mar 31. Diabetes Technol Ther. 2016. PMID: 27031372
-
Hypoxemia and glycemic control in type 2 diabetes mellitus with extreme obesity.J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014 Sep;99(9):E1650-4. doi: 10.1210/jc.2014-1260. Epub 2014 Jun 17. J Clin Endocrinol Metab. 2014. PMID: 24937534
-
The benefits of hypoglycemic therapy for patients with obstructive sleep apnea.Sleep Breath. 2024 Jun;28(3):1355-1363. doi: 10.1007/s11325-024-03015-2. Epub 2024 Mar 15. Sleep Breath. 2024. PMID: 38489146 Review.
Cited by
-
Upper airway and hyoid bone-related morphological parameters associated with the apnea-hypopnea index and lowest nocturnal oxygen saturation: a cephalometric analysis.BMC Oral Health. 2025 Apr 17;25(1):583. doi: 10.1186/s12903-025-05969-5. BMC Oral Health. 2025. PMID: 40247217 Free PMC article.
-
Sleep-Disordered Breathing and Interactions with Opioids: A Narrative Review.J Clin Med. 2025 Jul 4;14(13):4758. doi: 10.3390/jcm14134758. J Clin Med. 2025. PMID: 40649133 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-Induced Insulin Resistance Mediates the Elevated Cardiovascular Risk in Patients with Obstructive Sleep Apnea: A Comprehensive Review.Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024 Jun 25;25(6):231. doi: 10.31083/j.rcm2506231. eCollection 2024 Jun. Rev Cardiovasc Med. 2024. PMID: 39076340 Free PMC article. Review.
References
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical