Developing a music-based digital therapeutic to help manage the neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia
- PMID: 36744277
- PMCID: PMC9895844
- DOI: 10.3389/fdgth.2023.1064115
Developing a music-based digital therapeutic to help manage the neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia
Abstract
The greying of the world is leading to a rapid acceleration in both the healthcare costs and caregiver burden that are associated with dementia. There is an urgent need to develop new, easily scalable modalities of support. This perspective paper presents the theoretical background, rationale, and development plans for a music-based digital therapeutic to manage the neuropsychiatric symptoms of dementia, particularly agitation and anxiety. We begin by presenting the findings of a survey we conducted with key opinion leaders. The findings highlight the value of a music-based digital therapeutic for treating neuropsychiatric symptoms, particularly agitation and anxiety. We then consider the neural substrates of these neuropsychiatric symptoms before going on to evaluate randomized control trials on the efficacy of music-based interventions in their treatment. Finally, we present our development plans for the adaptation of an existing music-based digital therapeutic that was previously shown to be efficacious in the treatment of adult anxiety symptoms.
Keywords: agitation; anxiety; artificial intelligence; dementia; digital therapeutics; music; neuropsychiatric symptoms.
© 2023 Russo, Mallik, Thomson, de Raadt St. James, Dupuis and Cohen.
Conflict of interest statement
FR has served as an advisor for LUCID since 2018 and as Chief Science Officer since 2021. He has been granted stock options, which may qualify him to financially benefit from commercial applications of the technology considered here. AM, ZT and AR are full-time employees of LUCID and have also been granted stock options, which may qualify them to financially benefit from commercial applications of the technology considered here. The remaining authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
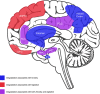
References
-
- Organization WH. Dementia (2022) [updated 2022–09–20; cited 2022 2022–09–24]. Available at: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia
-
- Reinhard SC, Given B, Petlick NH, Bemis A. Supporting family caregivers in providing care. Patient Safety and Quality: An Evidence-Based Handbook for Nurses. (2008. - PubMed
-
- Pedroza P, Miller-Petrie MK, Chen C, Chakrabarti S, Chapin A, Hay S, et al. Global and regional spending on dementia care from 2000 to 2019 and expected future health spending scenarios from 2020 to 2050: an economic modelling exercise. eClinMed. (2022) 45:101337. 10.1016/j.eclinm.2022.101337 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

