Thermal plasma processing of Moringa oleifera biochars: adsorbents for fluoride removal from water
- PMID: 36744284
- PMCID: PMC9890545
- DOI: 10.1039/d2ra07514h
Thermal plasma processing of Moringa oleifera biochars: adsorbents for fluoride removal from water
Abstract
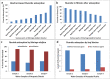
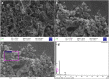
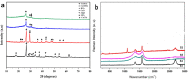
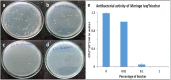
Anthropogenic activities accelerate fluoride contamination in groundwater, which largely affects public health. Though biochars have been explored for defluoridation, the plasma technology-based production of biochars has not received as considerable attention as other methods and it is also important that biochars be tested on groundwater samples. In the present study, for the first time, we report the preparation of biochars from different parts of Moringa oleifera using thermal plasma processing and demonstrate fluoride adsorption in both synthetic and contaminated groundwater. Water samples were collected from different locations in Nuapada district of Odisha such as Kotamal-Makardampada (20°24'46''N 82°37'19''E), Pandrapathar (20°34'41''N 82°39'25''E), Karlakot-Kadobhata (20°22'52''N 82°37'24''E), Kotamal-Jhakarpada (20°24'35''N 82°37'20''E), and Dohelpada (20°33'50''N 82°38'57''E). The Moringa leaf samples are processed at 1600 °C for 3 min in an inert atmosphere under a continuous flow of argon to get suitable biochars. The plasma-synthesized biochars contain larger exposed surfaces, which are efficient for the adsorption of fluoride. The prepared biochars were highly porous, amorphous, and contain > 72% carbon, which increases the efficiency of defluoridation due to the surface adsorbate site exposed. XRD of the samples showed the presence of calcium hydroxide, magnesium oxide, and calcium oxide, and large peaks of carbon. Raman data showed the double bond of carbon with oxygen in the form of carbonyl bonds, thioether, and sulfhydryl bonds, which contribute to the protonated site for the adsorption of fluoride, and assist in water penetration and swelling of biochars. The biochar of Moringa oleifera is very efficient for the adsorption of fluoride from standard samples as well as groundwater samples up to a concentration of 6 ppm. Conclusively, the present investigation shows that Moringa oleifera leaves are a good alternative adsorbent that could be used for the removal of fluoride from groundwater samples with > 85% removal in 18 h using 1 g biochar for 100 mL or 10 g biochar for 1 L water containing 4 ppm fluoride. To our knowledge, this is the first report on the thermal plasma-based production of Moringa biochars for the removal of fluoride from drinking water.
This journal is © The Royal Society of Chemistry.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Figures

References
-
- Saralakumari D. Rao P. R. Endemic fluorosis in the village Ralla Anantapuram in Andhra Pradesh: An epidemiological study. Fluoride – Q. Rep. 1993;26:177–180.
-
- Chowdhury A. Adak M. K. Mukherjee A. Dhak P. Khatun J. Dhak D. A critical review on geochemical and geological aspects of fluoride belts, fluorosis and natural materials and other sources for alternatives to fluoride exposure. J. Hydrol. 2019;574:333–359. doi: 10.1016/j.jhydrol.2019.04.033. - DOI
-
- Banks D. Reimann C. Røyset O. Skarphagen H. Sæther O. M. Natural concentrations of major and trace elements in some Norwegian bedrock groundwaters. Appl. Geochem. 1995;10(1):1–16. doi: 10.1016/0883-2927(94)00046-9. - DOI
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

