Reaction Dynamics in the Chrimson Channelrhodopsin: Observation of Product-State Evolution and Slow Diffusive Protein Motions
- PMID: 36745035
- PMCID: PMC9940203
- DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpclett.2c03110
Reaction Dynamics in the Chrimson Channelrhodopsin: Observation of Product-State Evolution and Slow Diffusive Protein Motions
Abstract
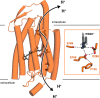
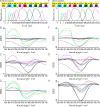
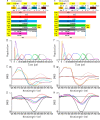
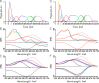
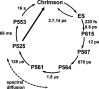
Chrimson is a red-light absorbing channelrhodopsin useful for deep-tissue optogenetics applications. Here, we present the Chrimson reaction dynamics from femtoseconds to seconds, analyzed with target analysis methods to disentangle spectrally and temporally overlapping excited- and product-state dynamics. We found multiple phases ranging from ≈100 fs to ≈20 ps in the excited-state decay, where spectral features overlapping with stimulated emission components were assigned to early dynamics of K-like species on a 10 ps time scale. Selective excitation at the maximum or the blue edge of the absorption spectrum resulted in spectrally distinct but kinetically similar excited-state and product-state species, which gradually became indistinguishable on the μs to 100 μs time scales. Hence, by removing specific protein conformations within an inhomogeneously broadened ensemble, we resolved slow protein backbone and amino acid side-chain motions in the dark that underlie inhomogeneous broadening, demonstrating that the latter represents a dynamic interconversion between protein substates.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
References
-
- Hochbaum D. R.; Zhao Y.; Farhi S. L.; Klapoetke N.; Werley C. A.; Kapoor V.; Zou P.; Kralj J. M.; Maclaurin D.; Smedemark-Margulies N.; Saulnier J. L.; Boulting G. L.; Straub C.; Cho Y. K.; Melkonian M.; Wong G. K. S.; Harrison D. J.; Murthy V. N.; Sabatini B. L.; Boyden E. S.; Campbell R. E.; Cohen A. E. All-optical electrophysiology in mammalian neurons using engineered microbial rhodopsins. Nat. Methods 2014, 11 (8), 825–833. 10.1038/nmeth.3000. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Klapoetke N. C.; Murata Y.; Kim S. S.; Pulver S. R.; Birdsey-Benson A.; Cho Y. K.; Morimoto T. K.; Chuong A. S.; Carpenter E. J.; Tian Z.; Wang J.; Xie Y.; Yan Z.; Zhang Y.; Chow B. Y.; Surek B.; Melkonian M.; Jayaraman V.; Constantine-Paton M.; Wong G. K.-S.; Boyden E. S. Independent optical excitation of distinct neural populations. Nat. Methods 2014, 11 (3), 338–46. 10.1038/nmeth.2836. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

