Benefit of Advanced 3D DSA and MRI/CT Fusion in Neurovascular Pathology
- PMID: 36745215
- PMCID: PMC10449735
- DOI: 10.1007/s00062-022-01260-0
Benefit of Advanced 3D DSA and MRI/CT Fusion in Neurovascular Pathology
Abstract
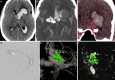
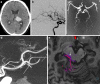
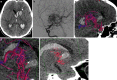
Digital subtraction angiography provides excellent spatial and temporal resolution; however, it lacks the capability to depict the nonvascular anatomy of the brain and spinal cord.A review of the institutional database identified five patients in whom a new integrated fusion workflow of cross-sectional imaging and 3D rotational angiography (3DRA) provided important diagnostic information and assisted in treatment planning. These included two acutely ruptured brain arteriovenous malformations (AVM), a small superficial brainstem AVM after radiosurgery, a thalamic microaneurysm, and a spine AVM, and fusion was crucial for diagnosis and influenced further treatment.Fusion of 3DRA and cross-sectional imaging may help to gain a deeper understanding of neurovascular diseases. This is advantageous for planning and providing treatment and, most importantly, may harbor the potential to minimize complication rates. Integrating image fusion in the work-up of cerebrovascular diseases is likely to have a major impact on the neurovascular field in the future.
Keywords: AVM; Aneurysm; Image fusion; Intracerebral hemorrhage; Rotational angiography.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
T. Dobrocky, M. Matzinger, E.I. Piechowiak, J. Kaesmacher, S. Pilgram-Pastor, J. Goldberg, D. Bervini, T. Klail, V.M. Pereira, W. Z’Graggen, A. Raabe, P. Mordasini and J. Gralla declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures


References
-
- Suzuki H, Shimizu S, Maki H, Maeda M, Sakaida H, Trousset Y, et al. Role of image fusion combining three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography with magnetic resonance imaging in evaluation of unruptured cerebral aneurysms. Neurol Res. 2007;29:58–63. doi: 10.1179/174313206X153806. - DOI - PubMed
-
- Suzuki H, Maki H, Taki W. Evaluation of cerebral arteriovenous malformations using image fusion combining three-dimensional digital subtraction angiography with magnetic resonance imaging. Turk Neurosurg. 2012;22:341–345. - PubMed

