Cohort profile: The Clinical and Multi-omic (CAMO) cohort, part of the Norwegian Women and Cancer (NOWAC) study
- PMID: 36745618
- PMCID: PMC9901780
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0281218
Cohort profile: The Clinical and Multi-omic (CAMO) cohort, part of the Norwegian Women and Cancer (NOWAC) study
Abstract
Introduction: Breast cancer is the most common cancer worldwide and the leading cause of cancer related deaths among women. The high incidence and mortality of breast cancer calls for improved prevention, diagnostics, and treatment, including identification of new prognostic and predictive biomarkers for use in precision medicine.
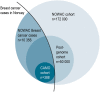
Material and methods: With the aim of compiling a cohort amenable to integrative study designs, we collected detailed epidemiological and clinical data, blood samples, and tumor tissue from a subset of participants from the prospective, population-based Norwegian Women and Cancer (NOWAC) study. These study participants were diagnosed with invasive breast cancer in North Norway before 2013 according to the Cancer Registry of Norway and constitute the Clinical and Multi-omic (CAMO) cohort. Prospectively collected questionnaire data on lifestyle and reproductive factors and blood samples were extracted from the NOWAC study, clinical and histopathological data were manually curated from medical records, and archived tumor tissue collected.
Results: The lifestyle and reproductive characteristics of the study participants in the CAMO cohort (n = 388) were largely similar to those of the breast cancer patients in NOWAC (n = 10 356). The majority of the cancers in the CAMO cohort were tumor grade 2 and of the luminal A subtype. Approx. 80% were estrogen receptor positive, 13% were HER2 positive, and 12% were triple negative breast cancers. Lymph node metastases were present in 31% at diagnosis. The epidemiological dataset in the CAMO cohort is complemented by mRNA, miRNA, and metabolomics analyses in plasma, as well as miRNA profiling in tumor tissue. Additionally, histological analyses at the level of proteins and miRNAs in tumor tissue are currently ongoing.
Conclusion: The CAMO cohort provides data suitable for epidemiological, clinical, molecular, and multi-omics investigations, thereby enabling a systems epidemiology approach to translational breast cancer research.
Copyright: © 2023 Delgado et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures


References
-
- WHO. Breast cancer now most common form of cancer: WHO taking action www.who.int: WHO; 2021 [updated March 2 2021; cited 2021 12. july]. https://www.who.int/news/item/03-02-2021-breast-cancer-now-most-common-f....
-
- GCO. Estimated number of deaths in 2020, worldwide, female, all ages: IARC; 2020 [cited 2021 12. july]. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/online-analysis-pie?v=2020&mode=cancer&mode_po....
-
- GCO. Breast gco.iarc.fr: IARC; 2020 [cited 2021 12. july]. https://gco.iarc.fr/today/data/factsheets/cancers/20-Breast-fact-sheet.pdf.
-
- ACS. Survival Rates for Breast Cancer Cancer.org: The American Cancer Society; updated January 27, 2021. https://www.cancer.org/cancer/breast-cancer/understanding-a-breast-cance....
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

