The effect of synbiotic supplementation on hypothyroidism: A randomized double-blind placebo controlled clinical trial
- PMID: 36745650
- PMCID: PMC9901790
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0277213
The effect of synbiotic supplementation on hypothyroidism: A randomized double-blind placebo controlled clinical trial
Abstract
Objective: We hypothesize that synbiotic supplementation could modulate the intestinal microbiota and subsequently, improve the condition of hypothyroid patients.
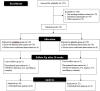
Methods: Fifty-six adult hypothyroid patients were recruited to this double-blind, placebo-controlled, randomized clinical trial. The intervention was 10 weeks of synbiotic (500 mg of 109 CFU/g probiotics plus fructo-oligosaccharide, n = 28) compared to placebo (lactose, magnesium stearate, talc, and silicon dioxide, n = 28). Randomization and allocation to trial groups were carried out using random number sequences drawn from https://sealedenvelope.com/. Primary outcomes were serum thyroid stimulating hormone (TSH) and free thyroxine (FT4), and secondary outcomes were depression, quality of life, and blood pressure (BP). P-values< 0.05 were considered statistically significant.
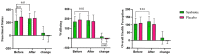
Results: Analysis on 51 patients who completed the trial showed that TSH and depression (p> 0.05) did not change significantly, while serum FT4 significantly increased in both groups (p = 0.03 and p = 0.02 in symbiotic and placebo respectively). A significant decrease in systolic BP occurred only in the synbiotic group (p = 0.05). Significant improvements occurred regarding different domains and areas of quality of life in the crude and adjusted analysis, including perceived mental health (p = 0.02), bodily pain (p = 0.02), general health perception (p = 0.002), and wellbeing (p = 0.002), which were significantly higher in the synbiotic group.
Conclusions: Ten-week supplementation with synbiotic had no favorable effect on depression and TSH, but it improved blood pressure and quality of life in patients with hypothyroidism. More trials are needed to support or reject these findings.
Trial registration: IRCT20210926052583N1, Iranian Registry of Clinical Trials (IRCT), registered October 1st, 2021.
Copyright: © 2023 Ramezani et al. This is an open access article distributed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution License, which permits unrestricted use, distribution, and reproduction in any medium, provided the original author and source are credited.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have declared that no competing interests exist.
Figures
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

