In Vitro and In Vivo Validation of CYP6A14 and CYP6N6 Participation in Deltamethrin Metabolic Resistance in Aedes albopictus
- PMID: 36746656
- PMCID: PMC9978559
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.22-0524
In Vitro and In Vivo Validation of CYP6A14 and CYP6N6 Participation in Deltamethrin Metabolic Resistance in Aedes albopictus
Abstract
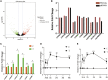
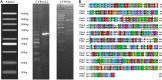
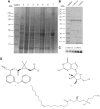
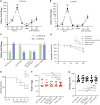
The extensive use of chemical insecticides for public health and agricultural purposes has increased the occurrence and development of insecticide resistance. This study used transcriptome sequencing to screen 10 upregulated metabolic detoxification enzyme genes from Aedes albopictus resistant strains. Of these, CYP6A14 and CYP6N6 were found to be substantially overexpressed in the deltamethrin-induced expression test, indicating their role in deltamethrin resistance in Ae. albopictus. Furthermore, the corresponding 60-kDa recombinant proteins, CYP6A14 and CYP6N6, were successfully expressed using the Escherichia coli expression system. Enzyme activity studies revealed that CYP6A14 (5.84 U/L) and CYP6N6 (6.3 U/L) have cytochrome P450 (CYP450) enzyme activity. In vitro, the metabolic analysis revealed that the recombinant proteins degraded deltamethrin into 1-oleoyl-sn-glycero-3-phosphoethanolamine and 2',2'-dibromo-2'-deoxyguanosine. Subsequently, the CYP450 genes in larvae of Ae. albopictus were silenced by RNA interference technology to study deltamethrin resistance in vivo. The silencing of CYP6A14 and CYP6N6 increased the mortality rate of mosquitoes without affecting their survival time, spawning quantity, hatching rate, and other normal life activities. Altogether, CYP6A14 and CYP6N6 belong to the CYP6 family and mutually increase deltamethrin resistance in Ae. albopictus.
Figures
Similar articles
-
Effects of deltamethrin exposure on the cytochrome P450 monooxygenases of Aedes albopictus (Skuse) larvae from a dengue-endemic region of northern part of West Bengal, India.Med Vet Entomol. 2024 Sep;38(3):269-279. doi: 10.1111/mve.12713. Epub 2024 Mar 13. Med Vet Entomol. 2024. PMID: 38478926
-
A symbiotic gut bacterium enhances Aedes albopictus resistance to insecticide.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022 Mar 4;16(3):e0010208. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0010208. eCollection 2022 Mar. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2022. PMID: 35245311 Free PMC article.
-
Preliminary Selection and Analysis of Deltamethrin-Resistant Strains of Aedes albopictus in the Laboratory.Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020 Sep;20(9):715-722. doi: 10.1089/vbz.2019.2584. Epub 2020 May 6. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2020. PMID: 32380934
-
Impact of deltamethrin-resistance in Aedes albopictus on its fitness cost and vector competence.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021 Apr 27;15(4):e0009391. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0009391. eCollection 2021 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2021. PMID: 33905415 Free PMC article.
-
The Differential Metabolic Profiles Between Deltamethrin-Resistant and -Susceptible Strains of Aedes albopictus (Diptera: Culicidae) by 1H-NMR.J Med Entomol. 2021 May 15;58(3):1256-1263. doi: 10.1093/jme/tjaa273. J Med Entomol. 2021. PMID: 33367827 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Yunta C, Hemmings K, Stevenson B, Koekemoer LL, Matambo T, Pignatelli P, Voice M, Nász S, Paine MJI, 2019. Cross-resistance profiles of malaria mosquito P450s associated with pyrethroid resistance against WHO insecticides. Pestic Biochem Physiol 161: 61–67. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

