Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and their Relevance for the Deployment of Primaquine as a Radical Cure for Malaria
- PMID: 36746659
- PMCID: PMC9978548
- DOI: 10.4269/ajtmh.22-0468
Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms in Glucose-6-Phosphate Dehydrogenase and their Relevance for the Deployment of Primaquine as a Radical Cure for Malaria
Abstract
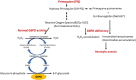
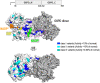
Malaria remains an important public health problem despite efforts to control it. Besides active transmission, relapsing malaria caused by dormant liver stages of Plasmodium vivax and Plasmodium ovale hypnozoites is a major hurdle in malaria control and elimination programs. Primaquine (PQ) is the most widely used drug for radical cure of malaria. Due to its anti-hypnozoite and gametocidal activity, PQ plays a key role in malaria relapse and transmission. The human enzyme glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase (G6PD) is crucial in determining the safety of PQ because G6PD-deficient individuals are prone to hemolysis if treated with PQ. Therefore, there is a need to study the prevalence of G6PD-deficient genetic variants in endemic populations to assess the risk of PQ treatment and the necessity to develop alternative treatments. In this work, we discuss the common G6PD variants, their varying enzymatic activity, and their distribution on the three-dimensional structure of G6PD. Our work highlights the important G6PD variants and the need for large-scale G6PD gene polymorphism studies to predict populations at risk of PQ-induced toxicity.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Effects of Host Genetic Polymorphisms on the Efficacy of the Radical Cure Malaria Drug Primaquine.Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2022 Jan 10;106(3):764-767. doi: 10.4269/ajtmh.21-1115. Am J Trop Med Hyg. 2022. PMID: 35008050 Free PMC article.
-
Primaquine ineligibility in anti-relapse therapy of Plasmodium vivax malaria: the problem of G6PD deficiency and cytochrome P-450 2D6 polymorphisms.Malar J. 2018 Jan 22;17(1):42. doi: 10.1186/s12936-018-2190-z. Malar J. 2018. PMID: 29357870 Free PMC article.
-
Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency prevalence and genetic variants in malaria endemic areas of Colombia.Malar J. 2016 May 26;15(1):291. doi: 10.1186/s12936-016-1343-1. Malar J. 2016. PMID: 27225440 Free PMC article.
-
Primaquine treatment and relapse in Plasmodium vivax malaria.Pathog Glob Health. 2016;110(1):1-8. doi: 10.1080/20477724.2015.1133033. Epub 2016 Feb 18. Pathog Glob Health. 2016. PMID: 27077309 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Use of primaquine and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency testing: Divergent policies and practices in malaria endemic countries.PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018 Apr 19;12(4):e0006230. doi: 10.1371/journal.pntd.0006230. eCollection 2018 Apr. PLoS Negl Trop Dis. 2018. PMID: 29672516 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- WHO , 2021. World Malaria Report 2021. Geneva, Switzerland: World Health Organization.
-
- Kojom Foko LP, Arya A, Sharma A, Singh V, 2021. Epidemiology and clinical outcomes of severe Plasmodium vivax malaria in India. J Infect 82: 231–246. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

