Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
- PMID: 36746784
- PMCID: PMC10040621
- DOI: 10.4093/dmj.2022.0346
Insulin Fact Sheet in Type 1 and 2 Diabetes Mellitus and Trends of Antidiabetic Medication Use in Insulin Users with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus: 2002 to 2019
Abstract
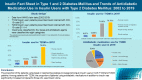
Background: This study investigated the trends of insulin use among Korean patients with type 1 diabetes mellitus (T1DM) and type 2 diabetes mellitus (T2DM). Changes in prescription of antidiabetic medications in T2DM patients taking insulin therapy were evaluated.
Methods: We analyzed data from the National Health Insurance Service database in Korea to evaluate the prevalence of insulin users and trends of insulin use in T1DM and T2DM patients from January 2002 to December 2019. We also investigated numbers and types of antidiabetic medications in insulin users with T2DM.
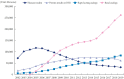
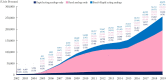
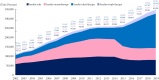
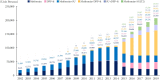
Results: The overall total number of insulin users increased from 2002 to 2019, reaching 348,254 for T2DM and 20,287 for T1DM in 2019 compared with 109,974 for T2DM and 34,972 for T1DM in 2002. The proportion of patients using basal analogs and short acting analogs have increased and those using human insulin, premixed insulin, or biphasic human insulin have decreased (rapid acting analogs: 71.85% and 24.12% in T1DM and T2DM, respectively, in 2019; basal analogs: 76.75% and 75.09% in T1DM and T2DM, respectively, in 2019). The use of other antidiabetic medication in addition to insulin increased for T2DM, especially in dual therapy, reaching up to 52.35% in 2019 compared with 16.72% in 2002.
Conclusion: The proportion of the patients using basal or rapid acting analogs increased among all insulin users in both T1DM and T2DM patients. Among patients with T2DM, the proportion of patients using antidiabetic medications in addition to insulin was significantly increased compared to those who used insulin alone.
Keywords: Diabetes mellitus, type 1; Diabetes mellitus, type 2; Hypoglycemic agents; Insulin.
Conflict of interest statement
Sang-Man Jin has been associate editor of the
Figures
Similar articles
-
Insulin therapy for diabetes mellitus: treatment regimens and associated costs.Diabetes Metab. 2012 Apr;38(2):156-63. doi: 10.1016/j.diabet.2011.10.003. Epub 2011 Dec 14. Diabetes Metab. 2012. PMID: 22172400
-
Cost-effectiveness of insulin degludec versus insulin glargine U100 in adults with type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Bulgaria.BMC Endocr Disord. 2019 Dec 3;19(1):132. doi: 10.1186/s12902-019-0460-6. BMC Endocr Disord. 2019. PMID: 31796048 Free PMC article.
-
Contrasting weight changes with LY2605541, a novel long-acting insulin, and insulin glargine despite similar improved glycaemic control in T1DM and T2DM.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014 Apr;16(4):351-6. doi: 10.1111/dom.12223. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2014. PMID: 24719911 Clinical Trial.
-
A Review of the Clinical Efficacy and Safety of Insulin Degludec and Glargine 300 U/mL in the Treatment of Diabetes Mellitus.Clin Ther. 2017 Aug;39(8S2):S12-S33. doi: 10.1016/j.clinthera.2017.01.007. Epub 2017 Feb 7. Clin Ther. 2017. PMID: 28187863 Review.
-
Screening and treatment of childhood type 1 and type 2 diabetes mellitus in Japan.Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2012 Oct;10 Suppl 1:51-61. Pediatr Endocrinol Rev. 2012. PMID: 23330246 Review.
Cited by
-
Adherence to the nutritional recommendations according to diabetes status in Korean adults: a cross-sectional study.BMC Public Health. 2024 Sep 27;24(1):2647. doi: 10.1186/s12889-024-20058-y. BMC Public Health. 2024. PMID: 39334162 Free PMC article.
-
In vitro α-Glucosidase Inhibition, Cytotoxicity, SAR, Swiss ADME Prediction and Molecular Docking Study of New N-Substituted Hydantoin Derivatives.ChemistryOpen. 2025 Apr;14(4):e202400119. doi: 10.1002/open.202400119. Epub 2025 Feb 3. ChemistryOpen. 2025. PMID: 39901517 Free PMC article.
-
Heterogeneity of continuous glucose monitoring features and their clinical associations in a type 2 diabetes population.Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025 Jul;27(7):3957-3966. doi: 10.1111/dom.16432. Epub 2025 May 19. Diabetes Obes Metab. 2025. PMID: 40390299 Free PMC article.
-
Evaluation of pharmacokinetic interactions between lobeglitazone, empagliflozin, and metformin in healthy subjects.Transl Clin Pharmacol. 2023 Mar;31(1):59-68. doi: 10.12793/tcp.2023.31.e4. Epub 2023 Mar 23. Transl Clin Pharmacol. 2023. PMID: 37034122 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in the Epidemiological Landscape of Diabetes in South Korea: Trends in Prevalence, Incidence, and Healthcare Expenditures.Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2024 Oct;39(5):669-677. doi: 10.3803/EnM.2024.2073. Epub 2024 Sep 25. Endocrinol Metab (Seoul). 2024. PMID: 39322188 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Diabetes Control and Complications Trial Research Group. Nathan DM, Genuth S, Lachin J, Cleary P, Crofford O, et al. The effect of intensive treatment of diabetes on the development and progression of long-term complications in insulindependent diabetes mellitus. N Engl J Med. 1993;329:977–86. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

