Dissecting and targeting noncanonical functions of EZH2 in multiple myeloma via an EZH2 degrader
- PMID: 36747009
- PMCID: PMC10040430
- DOI: 10.1038/s41388-023-02618-5
Dissecting and targeting noncanonical functions of EZH2 in multiple myeloma via an EZH2 degrader
Abstract
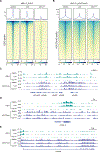
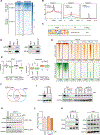
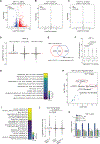
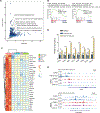
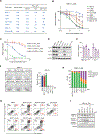
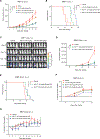
Multiple myeloma (MM) is the second most common hematological malignancy with poor prognosis. Enhancer of zeste homolog 2 (EZH2) is the enzymatic subunit of polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2), which catalyzes trimethylation of histone H3 lysine 27 (H3K27me3) for transcriptional repression. EZH2 have been implicated in numerous hematological malignancies, including MM. However, noncanonical functions of EZH2 in MM tumorigenesis are not well understood. Here, we uncovered a noncanonical function of EZH2 in MM malignancy. In addition to the PRC2-mediated and H3K27me3-dependent canonical function, EZH2 interacts with cMyc and co-localizes with gene activation-related markers, promoting MM tumorigenesis in a PRC2- and H3K27me3-independent manner. Both canonical EZH2-PRC2 and noncanonical EZH2-cMyc complexes can be effectively depleted in MM cells by MS177, an EZH2 degrader we reported previously, leading to profound activation of EZH2-PRC2-associated genes and simultaneous suppression of EZH2-cMyc oncogenic nodes. The MS177-induced degradation of both canonical EZH2-PRC2 and noncanonical EZH2-cMyc complexes also reactivated immune response genes in MM cells. Phenotypically, targeting of EZH2's both canonical and noncanonical functions by MS177 effectively suppressed the proliferation of MM cells both in vitro and in vivo. Collectively, this study uncovers a new noncanonical function of EZH2 in MM tumorigenesis and provides a novel therapeutic strategy, pharmacological degradation of EZH2, for treating EZH2-dependent MM.
© 2023. The Author(s), under exclusive licence to Springer Nature Limited.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interest statement
The Jin laboratory received research funds from Celgene Corporation, Levo Therapeutics, Inc., Cullgen, Inc. and Cullinan Oncology, Inc. J.J. is a cofounder and equity shareholder in Cullgen, Inc., a scientific cofounder and scientific advisory board member of Onsero Therapeutics, Inc., and a consultant for Cullgen, Inc., EpiCypher, Inc. and Accent Therapeutics, Inc.
Figures

References
-
- Cowan AJ, Green DJ, Kwok M, Lee S, Coffey DG, Holmberg LA et al. Diagnosis and Management of Multiple Myeloma: A Review. JAMA 2022; 327: 464–477. - PubMed
-
- van de Donk NWCJ, Pawlyn C, Yong KL. Multiple myeloma. The Lancet 2021; 397: 410–427. - PubMed
-
- Kuehl WM, Bergsagel PL. Multiple myeloma: evolving genetic events and host interactions. Nat Rev Cancer 2002; 2: 175–187. - PubMed
-
- Kyle RA, Therneau TM, Rajkumar SV, Offord JR, Larson DR, Plevak MF et al. A long-term study of prognosis in monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance. N Engl J Med 2002; 346: 564–569. - PubMed
-
- Morgan GJ, Walker BA, Davies FE. The genetic architecture of multiple myeloma. Nat Rev Cancer 2012; 12: 335–348. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

