Perivascular cells induce microglial phagocytic states and synaptic engulfment via SPP1 in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 36747024
- PMCID: PMC9991912
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01257-z
Perivascular cells induce microglial phagocytic states and synaptic engulfment via SPP1 in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
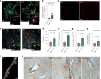
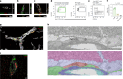
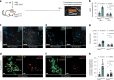
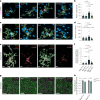
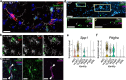
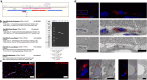
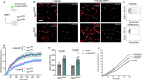
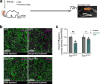
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by synaptic loss, which can result from dysfunctional microglial phagocytosis and complement activation. However, what signals drive aberrant microglia-mediated engulfment of synapses in AD is unclear. Here we report that secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1/osteopontin) is upregulated predominantly by perivascular macrophages and, to a lesser extent, by perivascular fibroblasts. Perivascular SPP1 is required for microglia to engulf synapses and upregulate phagocytic markers including C1qa, Grn and Ctsb in presence of amyloid-β oligomers. Absence of Spp1 expression in AD mouse models results in prevention of synaptic loss. Furthermore, single-cell RNA sequencing and putative cell-cell interaction analyses reveal that perivascular SPP1 induces microglial phagocytic states in the hippocampus of a mouse model of AD. Altogether, we suggest a functional role for SPP1 in perivascular cells-to-microglia crosstalk, whereby SPP1 modulates microglia-mediated synaptic engulfment in mouse models of AD.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures


Similar articles
-
Fibrillar Aβ triggers microglial proteome alterations and dysfunction in Alzheimer mouse models.Elife. 2020 Jun 8;9:e54083. doi: 10.7554/eLife.54083. Elife. 2020. PMID: 32510331 Free PMC article.
-
Ceftriaxone ameliorates hippocampal synapse loss by inhibiting microglial/macrophages activation in glial glutamate transporter-1 dependent manner in the APP/PS1 mouse model of Alzheimer's disease.Brain Res Bull. 2023 Aug;200:110683. doi: 10.1016/j.brainresbull.2023.110683. Epub 2023 Jun 8. Brain Res Bull. 2023. PMID: 37301482
-
Gossypetin ameliorates 5xFAD spatial learning and memory through enhanced phagocytosis against Aβ.Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022 Oct 21;14(1):158. doi: 10.1186/s13195-022-01096-3. Alzheimers Res Ther. 2022. PMID: 36271414 Free PMC article.
-
Microglia in Alzheimer's Disease: A Favorable Cellular Target to Ameliorate Alzheimer's Pathogenesis.Mediators Inflamm. 2022 Jun 2;2022:6052932. doi: 10.1155/2022/6052932. eCollection 2022. Mediators Inflamm. 2022. PMID: 35693110 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Emerging evidence of context-dependent synapse elimination by phagocytes in the CNS.J Leukoc Biol. 2024 Sep 2;116(3):511-522. doi: 10.1093/jleuko/qiae098. J Leukoc Biol. 2024. PMID: 38700080 Review.
Cited by
-
Single-cell sequencing reveals an important role of SPP1 and microglial activation in age-related macular degeneration.Front Cell Neurosci. 2024 Jan 8;17:1322451. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2023.1322451. eCollection 2023. Front Cell Neurosci. 2024. PMID: 38259505 Free PMC article.
-
DHCR24 reverses Alzheimer's disease-related pathology and cognitive impairment via increasing hippocampal cholesterol levels in 5xFAD mice.Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023 Jun 21;11(1):102. doi: 10.1186/s40478-023-01593-y. Acta Neuropathol Commun. 2023. PMID: 37344916 Free PMC article.
-
Advancements in Single-Cell RNA Sequencing Research for Neurological Diseases.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Nov;61(11):8797-8819. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-04126-3. Epub 2024 Apr 2. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38564138 Review.
-
Osteopontin drives neuroinflammation and cell loss in MAPT-N279K frontotemporal dementia patient neurons.Cell Stem Cell. 2024 May 2;31(5):676-693.e10. doi: 10.1016/j.stem.2024.03.013. Epub 2024 Apr 15. Cell Stem Cell. 2024. PMID: 38626772 Free PMC article.
-
Detrimental influence of Arginase-1 in infiltrating macrophages on poststroke functional recovery and inflammatory milieu.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025 Feb 18;122(7):e2413484122. doi: 10.1073/pnas.2413484122. Epub 2025 Feb 14. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2025. PMID: 39951507 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Kierdorf, K., Masuda, T., Jordão, M. J. C. & Prinz, M. Macrophages at CNS interfaces: ontogeny and function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci.20, 547–562 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Cserép, C. et al. Microglia monitor and protect neuronal function through specialized somatic purinergic junctions. Science367, 528–537 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Paolicelli, R. C. et al. Synaptic pruning by microglia is necessary for normal brain development. Science1456, 10–13 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

