Perivascular cells induce microglial phagocytic states and synaptic engulfment via SPP1 in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
- PMID: 36747024
- PMCID: PMC9991912
- DOI: 10.1038/s41593-023-01257-z
Perivascular cells induce microglial phagocytic states and synaptic engulfment via SPP1 in mouse models of Alzheimer's disease
Abstract
Alzheimer's disease (AD) is characterized by synaptic loss, which can result from dysfunctional microglial phagocytosis and complement activation. However, what signals drive aberrant microglia-mediated engulfment of synapses in AD is unclear. Here we report that secreted phosphoprotein 1 (SPP1/osteopontin) is upregulated predominantly by perivascular macrophages and, to a lesser extent, by perivascular fibroblasts. Perivascular SPP1 is required for microglia to engulf synapses and upregulate phagocytic markers including C1qa, Grn and Ctsb in presence of amyloid-β oligomers. Absence of Spp1 expression in AD mouse models results in prevention of synaptic loss. Furthermore, single-cell RNA sequencing and putative cell-cell interaction analyses reveal that perivascular SPP1 induces microglial phagocytic states in the hippocampus of a mouse model of AD. Altogether, we suggest a functional role for SPP1 in perivascular cells-to-microglia crosstalk, whereby SPP1 modulates microglia-mediated synaptic engulfment in mouse models of AD.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
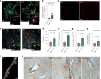
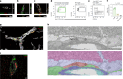
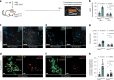
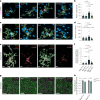


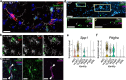
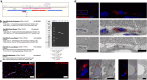
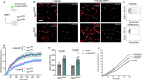
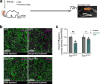
References
-
- Kierdorf, K., Masuda, T., Jordão, M. J. C. & Prinz, M. Macrophages at CNS interfaces: ontogeny and function in health and disease. Nat. Rev. Neurosci.20, 547–562 (2019). - PubMed
-
- Cserép, C. et al. Microglia monitor and protect neuronal function through specialized somatic purinergic junctions. Science367, 528–537 (2020). - PubMed
-
- Paolicelli, R. C. et al. Synaptic pruning by microglia is necessary for normal brain development. Science1456, 10–13 (2013). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

