Psychometric evaluation of the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale among Iranian population
- PMID: 36747165
- PMCID: PMC9902255
- DOI: 10.1186/s12888-023-04580-8
Psychometric evaluation of the Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale among Iranian population
Abstract
Background: The resilience construct is considered a personal trait composed of multiple aspects. Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale is a standard tool composed of five factors and 25 items. This study aimed to determine the psychometric properties of this scale.
Methods: In this cross-sectional study, after the scale translation, the factorial structural validity was assessed via the confirmatory factor analysis with 70 180 samples. Internal consistency, composite reliability, convergent validity were assessed by calculating Cronbach's alpha, composite reliability, maximum reliability, and Average Variance Extracted. The discriminant validity was assessed using Heterotrait-monotrait ratio of correlations matrix and also, measure invariance was evaluated.
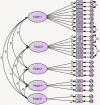
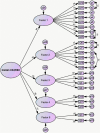
Results: The original five-factor model had good model fit indices but due to low factor loading of item 2 and 20, the model was modified. The Cronbach's alpha and composite reliability for four factors were above 0.7 (except for factor 5). The convergent validity for all five factors were achieved. Between factors 1 with 2 and 4, 2 with 3 and 4 discriminant validity was not established (correlations > 0.9) and the results suggested that there might be a second-order latent construct behind these factors. Therefore, a second-order assessment was performed. The results of the second-order latent construct assessment showed a good goodness-of fit and strong measurement invariance for both men and women.
Conclusion: The 23-item version of Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale is a reliable and valid scale to measure resilience as a complex construct in the Iran context.
Keywords: Connor-Davidson Resilience Scale; Iran; Psychological resilience; Psychometric; Questionnaire design.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
References
-
- Knipscheer J, Sleijpen M, Frank L, de Graaf R, Kleber R, ten Have M, et al. Prevalence of Potentially Traumatic Events, Other Life Events and Subsequent Reactions Indicative for Posttraumatic Stress Disorder in the Netherlands: A General Population Study Based on the Trauma Screening Questionnaire. Int J Environ Res Public Health. 2020;17(5):1725. doi: 10.3390/ijerph17051725. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ayed N, Toner S, Priebe S. Conceptualizing resilience in adult mental health literature: A systematic review and narrative synthesis. Psychol Psychother Theory Res Pract. 2019;92(3):299–341. - PubMed
-
- Zautra AJ, Hall JS, Murray KE. The Resilience Solutions G. Resilience: a new integrative approach to health and mental health research. Health Psychol Rev. 2008;2(1):41–64.