HNRNPL induced circFAM13B increased bladder cancer immunotherapy sensitivity via inhibiting glycolysis through IGF2BP1/PKM2 pathway
- PMID: 36747239
- PMCID: PMC9901087
- DOI: 10.1186/s13046-023-02614-3
HNRNPL induced circFAM13B increased bladder cancer immunotherapy sensitivity via inhibiting glycolysis through IGF2BP1/PKM2 pathway
Abstract
Background: The response rate to immunotherapy in patients with bladder cancer (BCa) remains relatively low. Considering the stable existence and important functions in tumour metabolism, the role of circRNAs in regulating immune escape and immunotherapy sensitivity is receiving increasing attention.
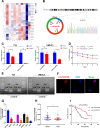
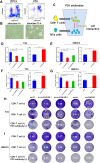
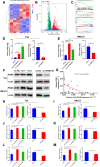
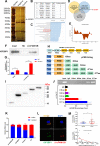
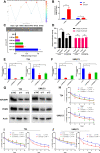
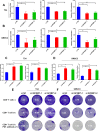
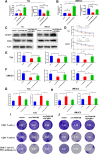
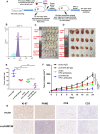
Methods: Circular RNA (circRNA) sequencing was performed on five pairs of BCa samples, and circFAM13B (hsa_circ_0001535) was screened out because of its remarkably low expression in BCa. Further mRNA sequencing was conducted, and the association of circFAM13B with glycolysis process and CD8+ T cell activation was confirmed. The functions of circFAM13B were verified by proliferation assays, glycolysis assays, BCa cells-CD8+ T cell co-culture assays and tumorigenesis experiment among human immune reconstitution NOG mice. Bioinformatic analysis, RNA-protein pull down, mass spectrometry, RNA immunoprecipitation, luciferase reporter assay and fluorescence in situ hybridization were performed to validate the HNRNPL/circFAM13B/IGF2BP1/PKM2 cascade.
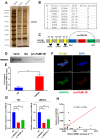
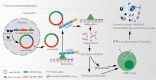
Results: Low expression of circFAM13B was observed in BCa, and it was positively associated with lower tumour stage and better prognosis among patients with BCa. The function of CD8+ T cells was promoted by circFAM13B, and it could attenuate the glycolysis of BCa cells and reverse the acidic tumour microenvironment (TME). The production of granzyme B and IFN-γ was improved, and the immunotherapy (PD-1 antibodies) sensitivity was facilitated by the inhibition of acidic TME. Mechanistically, circFAM13B was competitively bound to the KH3-4 domains of IGF2BP1 and subsequently reduced the binding of IGF2BP1 and PKM2 3'UTR. Thus, the stability of the PKM2 mRNA decreased, and glycolysis-induced acidic TME was inhibited. The generation of circFAM13B was explored by confirming whether heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein L (HNRNPL) could promote circFAM13B formation via pre-mRNA back-splicing.
Conclusions: HNRNPL-induced circFAM13B could repress immune evasion and enhance immunotherapy sensitivity by inhibiting glycolysis and acidic TME in BCa through the novel circFAM13B/IGF2BP1/PKM2 cascade. Therefore, circFAM13B can be used as a biomarker for guiding the immunotherapy among patients with BCa.
Keywords: Bladder cancer; Glycolysis; IGF2BP1; Immunosensitivity; PKM2; circFAM13B.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures
Similar articles
-
CircZNF609 inhibited bladder cancer immunotherapy sensitivity via enhancing fatty acid uptake through IGF2BP2/CD36 pathway.Int Immunopharmacol. 2024 Aug 20;137:112485. doi: 10.1016/j.intimp.2024.112485. Epub 2024 Jun 14. Int Immunopharmacol. 2024. PMID: 38878487
-
Lysine N-methyltransferase SETD7 promotes bladder cancer progression and immune escape via STAT3/PD-L1 cascade.Int J Biol Sci. 2023 Jul 16;19(12):3744-3761. doi: 10.7150/ijbs.87182. eCollection 2023. Int J Biol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37564199 Free PMC article.
-
circSOBP Inhibits Bladder Cancer Proliferation and Metastasis by Regulating the miR-200a-3p/PTEN Axis and Participating in the Immune Response.Cell Transplant. 2023 Jan-Dec;32:9636897231165874. doi: 10.1177/09636897231165874. Cell Transplant. 2023. PMID: 37026617 Free PMC article.
-
Expression profiles, biological functions and clinical significance of circRNAs in bladder cancer.Mol Cancer. 2021 Jan 4;20(1):4. doi: 10.1186/s12943-020-01300-8. Mol Cancer. 2021. PMID: 33397425 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Regulation of the tumor immune microenvironment by cancer-derived circular RNAs.Cell Death Dis. 2023 Feb 16;14(2):132. doi: 10.1038/s41419-023-05647-w. Cell Death Dis. 2023. PMID: 36797245 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
KLF7 reverses ox-LDL-induced ferroptosis in HMEC-1 cells through transcriptionally activating ALKBH5 to inhibit the m6A modification of ACSL4.Cytotechnology. 2024 Dec;76(6):653-666. doi: 10.1007/s10616-024-00641-2. Epub 2024 Jul 1. Cytotechnology. 2024. PMID: 39435423
-
DeepGR: a deep-learning prognostic model based on glycolytic radiomics for non-small cell lung cancer.Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024 Oct 31;13(10):2746-2760. doi: 10.21037/tlcr-24-716. Epub 2024 Oct 17. Transl Lung Cancer Res. 2024. PMID: 39507025 Free PMC article.
-
hnRNPL phase separation activates PIK3CB transcription and promotes glycolysis in ovarian cancer.Nat Commun. 2025 May 24;16(1):4828. doi: 10.1038/s41467-025-60115-7. Nat Commun. 2025. PMID: 40413189 Free PMC article.
-
Platelet-derived circFAM13B associated with anti-platelet responsiveness of ticagrelor in patients with acute coronary syndrome.Thromb J. 2024 Jun 21;22(1):53. doi: 10.1186/s12959-024-00620-9. Thromb J. 2024. PMID: 38907258 Free PMC article.
-
Recent Advances in the Mutual Regulation of m6A Modification and Non-Coding RNAs in Atherosclerosis.Int J Gen Med. 2025 Feb 25;18:1047-1073. doi: 10.2147/IJGM.S508197. eCollection 2025. Int J Gen Med. 2025. PMID: 40026815 Free PMC article. Review.
References
-
- Antoni S, Ferlay J, Soerjomataram I, Znaor A, Jemal A, Bray F. Bladder cancer incidence and mortality: a global overview and recent trends. Eur Urol. 2017;71(1):96–108. - PubMed
-
- van Rhijn BW, Burger M, Lotan Y, Solsona E, Stief CG, Sylvester RJ, et al. Recurrence and progression of disease in non-muscle-invasive bladder cancer: from epidemiology to treatment strategy. Eur Urol. 2009;56(3):430–442. - PubMed
-
- Lenis AT, Lec PM, Chamie K, Mshs MD. Bladder cancer: a review. JAMA. 2020;324(19):1980–1991. - PubMed
-
- Patel VG, Oh WK, Galsky MD. Treatment of muscle-invasive and advanced bladder cancer in 2020. CA Cancer J Clin. 2020;70(5):404–423. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

