A Prospective Multi-centric Study of Acceptance, Insertion and Follow-Up of Postpartum Insertions of IUCD
- PMID: 36747973
- PMCID: PMC9893971
- DOI: 10.1007/s13224-022-01738-4
A Prospective Multi-centric Study of Acceptance, Insertion and Follow-Up of Postpartum Insertions of IUCD
Abstract
Purpose of the study: The unmet need for contraception in the postpartum period is a major challenge in our country. Unintended pregnancies are highest in the first year after birth, and postpartum IUCD insertion is an effective way to counter this problem. This study was planned to build up data for acceptance and follow-up of postpartum IUCD insertions.
Methods: The present study has included data of PPIUCD insertions and follow-up from seven institutions over a period of 6 months. The case recruitment lasted for 3 months, including only those who had PPIUCD insertions in this period, and they were followed up for a period of 6 months. The follow-up of patients was at 6 weeks and 6 months. All issues were addressed including side effects, expulsions, myths surrounding the device, etc., along with routine postnatal care.
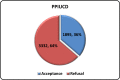
Results and conclusion: There were 5227 deliveries and 1895 insertions. The acceptance rate was 36%, and a follow-up at 6 weeks and 6 months showed up an expulsion rate of approximately 4% and a removal rate of 5%. Overall, at the end of 6 months we have a continuation rate of 90%. This shows that a dedicated approach to postpartum contraception will definitely bring down incidence of unintended pregnancies.
Keywords: Contraception; Intra caesarean insertion; LARC; PPIUCD; Post partum contraception; Post placental insertion.
© Federation of Obstetric & Gynecological Societies of India 2023. Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interestNone declared.Ethical ApprovalThe study was approved by the Institutional Ethics Committee of each hospital. The authors are committed to and have fulfilled all the guidelines mentioned in the Helsinki Declaration for scientific research on clinical subjects, and we stand by it in all future references and citations for this article. The authors have no potential conflicts of interest to disclose. This research involved human participants and no animals. Informed consent was taken from all participants from all patients involved in the study.
References
-
- Nelson A. Intrauterine contraceptive. J Obstet Gynecol. 2008;6:219–24.
-
- Ashok S, John S, Jayanti MT. The KAP-gap in Nepal: reasons for non-use of contraception among couples with an unmet need for family planning. Asia Pac Popul J. 2000;6:25–38. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials