QSM Throughout the Body
- PMID: 36748806
- PMCID: PMC10192074
- DOI: 10.1002/jmri.28624
QSM Throughout the Body
Abstract
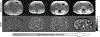
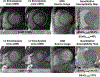
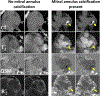
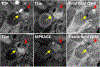
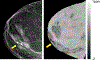
Magnetic materials in tissue, such as iron, calcium, or collagen, can be studied using quantitative susceptibility mapping (QSM). To date, QSM has been overwhelmingly applied in the brain, but is increasingly utilized outside the brain. QSM relies on the effect of tissue magnetic susceptibility sources on the MR signal phase obtained with gradient echo sequence. However, in the body, the chemical shift of fat present within the region of interest contributes to the MR signal phase as well. Therefore, correcting for the chemical shift effect by means of water-fat separation is essential for body QSM. By employing techniques to compensate for cardiac and respiratory motion artifacts, body QSM has been applied to study liver iron and fibrosis, heart chamber blood and placenta oxygenation, myocardial hemorrhage, atherosclerotic plaque, cartilage, bone, prostate, breast calcification, and kidney stone.
Keywords: body imaging; quantitative imaging; quantitative susceptibility mapping.
© 2023 International Society for Magnetic Resonance in Medicine.
Figures
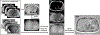
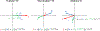

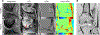


References
-
- Harada T, Kudo K, Fujima N, et al. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping: Basic Methods and Clinical Applications. Radiographics 2022;42(4):1161–1176. - PubMed
-
- Vinayagamani S, Sheelakumari R, Sabarish S, et al. Quantitative Susceptibility Mapping: Technical Considerations and Clinical Applications in Neuroimaging. J Magn Reson Imaging 2021;53(1):23–37. - PubMed
-
- Haacke EM, Liu S, Buch S, Zheng W, Wu D, Ye Y. Quantitative susceptibility mapping: current status and future directions. Magn Reson Imaging 2015;33(1):1–25. - PubMed
-
- Boyacioglu R, Wang C, Ma D, McGivney DF, Yu X, Griswold MA. 3D magnetic resonance fingerprinting with quadratic RF phase. Magn Reson Med 2021;85(4):2084–2094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

