The molecular pathogenesis of craniopharyngiomas
- PMID: 36748936
- PMCID: PMC10689043
- DOI: 10.20945/2359-3997000000600
The molecular pathogenesis of craniopharyngiomas
Abstract
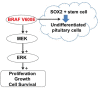
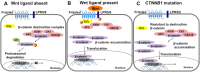
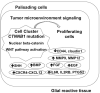
Research from the last 20 years has provided important insights into the molecular pathogenesis of craniopharyngiomas (CPs). Besides the well-known clinical and histological differences between the subtypes of CPs, adamantinomatous (ACP) and papillary (PCP) craniopharyngiomas, other molecular differences have been identified, further elucidating pathways related to the origin and development of such tumors. The present minireview assesses current knowledge on embryogenesis and the genetic, epigenetic, transcriptomic, and signaling pathways involved in the ACP and PCP subtypes, revealing the similarities and differences in their profiles. ACP and PCP subtypes can be identified by the presence of mutations in CTNNB1 and BRAF genes, with prevalence around 60% and 90%, respectively. Therefore, β-catenin accumulates in the nucleus-cytoplasm of cell clusters in ACPs and, in PCPs, cell immunostaining with specific antibody against the V600E-mutated protein can be seen. Distinct patterns of DNA methylation further differentiate ACPs and PCPs. In addition, research on genetic and epigenetic changes and tumor microenvironment specificities have further clarified the development and progression of the disease. No relevant transcriptional differences in ACPs have emerged between children and adults. In conclusion, ACPs and PCPs present diverse genetic signatures and each subtype is associated with specific signaling pathways. A better understanding of the pathways related to the growth of such tumors is paramount for the development of novel targeted therapeutic agents.
Keywords:
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosure: no potential conflict of interest relevant to this article was reported.
Figures
References
-
- Martins C, Silva JISM, Machado HR, de Castro M. In: Neuroendocrinologia – SBEM . Garmes HM, Boguszewski CL, editors. São Paulo: Clannad; 2020. Craniofaringioma: Epidemiologia, classificação e bases moleculares; pp. 141–148.
-
- Nielsen EH, Feldt-Rasmussen U, Poulsgaard L, Kristensen L, Astrup J, Jørgensen JO, et al. Incidence of craniopharyngioma in Denmark (n = 189) and estimated world incidence of craniopharyngioma in children and adults. J Neurooncol . 2011;104(3):755–763. - PubMed
-
- Weiner HL, Wisoff JH, Rosenberg ME, Kupersmith MJ, Cohen, Henry MPH, et al. Craniopharyngiomas: a clinicopathological analysis of factors predictive of recurrence and functional outcome. Neurosurgery . 1994;35(6):1001–1011. - PubMed
-
- Karavitaki N, Wass JAH. Craniopharyngiomas. Endocrinol Metab Clin North Am . 2008;37(1):173–193. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous
