Macrophages promote anti-androgen resistance in prostate cancer bone disease
- PMID: 36749798
- PMCID: PMC9948761
- DOI: 10.1084/jem.20221007
Macrophages promote anti-androgen resistance in prostate cancer bone disease
Abstract
Metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (PC) is the final stage of PC that acquires resistance to androgen deprivation therapies (ADT). Despite progresses in understanding of disease mechanisms, the specific contribution of the metastatic microenvironment to ADT resistance remains largely unknown. The current study identified that the macrophage is the major microenvironmental component of bone-metastatic PC in patients. Using a novel in vivo model, we demonstrated that macrophages were critical for enzalutamide resistance through induction of a wound-healing-like response of ECM-receptor gene expression. Mechanistically, macrophages drove resistance through cytokine activin A that induced fibronectin (FN1)-integrin alpha 5 (ITGA5)-tyrosine kinase Src (SRC) signaling cascade in PC cells. This novel mechanism was strongly supported by bioinformatics analysis of patient transcriptomics datasets. Furthermore, macrophage depletion or SRC inhibition using a novel specific inhibitor significantly inhibited resistant growth. Together, our findings elucidated a novel mechanism of macrophage-induced anti-androgen resistance of metastatic PC and a promising therapeutic approach to treat this deadly disease.
© 2023 Li et al.
Conflict of interest statement
Disclosures: J. Cao was sponsored by China Scholarship Council. A. Unciti-Broceta and N.O. Carragher reported grants from Nuvectis Pharma outside the submitted work; in addition, A. Unciti-Broceta and N.O. Carragher had patents to EP3298015B1, JP6684831B2, US10294227B2, CN107849050B, and CA3021550A1 licensed (Nuvectis Pharma). C. Sawyers reported personal fees from Novartis, Blueprint, Beigene, Foghorn, PMV, KSQ, Housey, Nextech, Column Group, Cellcarta, and Oric outside the submitted work; in addition, C. Sawyers had a patent to enzalutamide with royalties paid and a patent to apalutamide with royalties paid. B.Z. Qian reported personal fees from Medanexx Ltd and Nuvectis Pharma outside the submitted work. No other disclosures were reported.
Figures
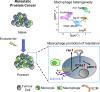
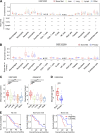
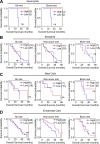
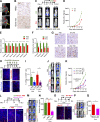
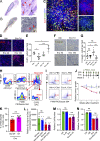
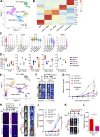
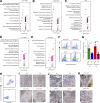
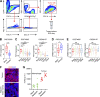

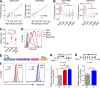
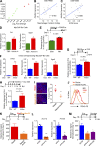
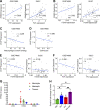
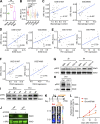
Comment in
-
Macrophages and bone metastasis.J Exp Med. 2023 Apr 3;220(4):e20222188. doi: 10.1084/jem.20222188. Epub 2023 Feb 24. J Exp Med. 2023. PMID: 36828392 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Antonarakis, E.S., Heath E.I., Posadas E.M., Yu E.Y., Harrison M.R., Bruce J.Y., Cho S.Y., Wilding G.E., Fetterly G.J., Hangauer D.G., et al. . 2013. A phase 2 study of KX2-391, an oral inhibitor of Src kinase and tubulin polymerization, in men with bone-metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer. Cancer Chemother. Pharmacol. 71:883–892. 10.1007/s00280-013-2079-z - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Araujo, J.C., Trudel G.C., Saad F., Armstrong A.J., Yu E.Y., Bellmunt J., Wilding G., McCaffrey J., Serrano S.V., Matveev V.B., et al. . 2013. Docetaxel and dasatinib or placebo in men with metastatic castration-resistant prostate cancer (READY): A randomised, double-blind phase 3 trial. Lancet Oncol. 14:1307–1316. 10.1016/S1470-2045(13)70479-0 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

