JNK signaling in pioneer neurons organizes ventral nerve cord architecture in Drosophila embryos
- PMID: 36750572
- PMCID: PMC9905486
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-36388-1
JNK signaling in pioneer neurons organizes ventral nerve cord architecture in Drosophila embryos
Abstract
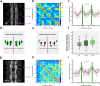
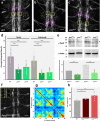
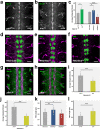
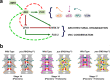
Morphogenesis of the Central Nervous System (CNS) is a complex process that obeys precise architectural rules. Yet, the mechanisms dictating these rules remain unknown. Analyzing morphogenesis of the Drosophila embryo Ventral Nerve Cord (VNC), we observe that a tight control of JNK signaling is essential for attaining the final VNC architecture. JNK signaling in a specific subset of pioneer neurons autonomously regulates the expression of Fasciclin 2 (Fas 2) and Neurexin IV (Nrx IV) adhesion molecules, probably via the transcription factor zfh1. Interfering at any step in this cascade affects fasciculation along pioneer axons, leading to secondary cumulative scaffolding defects during the structural organization of the axonal network. The global disorder of architectural landmarks ultimately influences nervous system condensation. In summary, our data point to JNK signaling in a subset of pioneer neurons as a key element underpinning VNC architecture, revealing critical milestones on the mechanism of control of its structural organization.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures



References
-
- Arendt D, Tosches MA, Marlow H. From nerve net to nerve ring, nerve cord and brain–evolution of the nervous system. Nat. Rev. Neurosci. 2016;17:61–72. - PubMed
-
- Qing Yu ZL, Chuanzi OuYang, Lingjun Li. Biologically Active Peptides in Invertebrates: Discovery and Functional Studies. In: Colloquium Series on neuropeptides). Morgan & Claypool Publishers (2015).
-
- Leise EM. Modular construction of nervous systems: a basic principle of design for invertebrates and vertebrates. Brain Res. Rev. 1990;15:1–23. - PubMed
-
- Redies C, Puelles L. Modularity in vertebrate brain development and evolution. BioEssays. 2001;23:1100–1111. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

