Association Between Hypocholesterolemia and Mortality in Critically Ill Patients With Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36751516
- PMCID: PMC9894355
- DOI: 10.1097/CCE.0000000000000860
Association Between Hypocholesterolemia and Mortality in Critically Ill Patients With Sepsis: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
To ascertain the association between cholesterol and triglyceride levels on ICU admission and mortality in patients with sepsis.
Data sources: Systematic review and meta-analysis of published studies on PubMed and Embase.
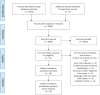
Study selection: All observational studies reporting ICU admission cholesterol and triglyceride levels in critically ill patients with sepsis were included. Authors were contacted for further data.
Data extraction: Eighteen observational studies were identified, including 1,283 patients with a crude overall mortality of 33.3%. Data were assessed using Revman (Version 5.1, Cochrane Collaboration, Oxford, United Kingdom) and presented as mean difference (MD) with 95% CIs, p values, and I 2 values.
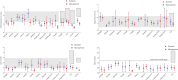
Data synthesis: Admission levels of total cholesterol (17 studies, 1,204 patients; MD = 0.52 mmol/L [0.27-0.77 mmol/L]; p < 0.001; I 2 = 91%), high-density lipoprotein (HDL)-cholesterol (14 studies, 991 patients; MD = 0.08 mmol/L [0.01-0.15 mmol/L]; p = 0.02; I 2 = 61%), and low-density lipoprotein (LDL)-cholesterol (15 studies, 1,017 patients; MD = 0.18 mmol/L [0.04-0.32 mmol/L]; p = 0.01; I 2 = 71%) were significantly lower in eventual nonsurvivors compared with survivors. No association was seen between admission triglyceride levels and mortality (15 studies, 1,070 patients; MD = 0.00 mmol/L [-0.16 to 0.15 mmol/L]; p = -0.95; I 2 = 79%).
Conclusions: Mortality was associated with lower levels of total cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol, and LDL-cholesterol, but not triglyceride levels, in patients admitted to ICU with sepsis. The impact of cholesterol replacement on patient outcomes in sepsis, particularly in at-risk groups, merits investigation.
Keywords: cholesterol levels; intensive care unit; lipids; sepsis; triglycerides.
Copyright © 2023 The Authors. Published by Wolters Kluwer Health, Inc. on behalf of the Society of Critical Care Medicine.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors have disclosed that they do not have any potential conflicts of interest.
Figures

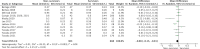


References
-
- Golucci APBS, Marson FAL, Ribeiro AF, et al. : Lipid profile associated with the systemic inflammatory response syndrome and sepsis in critically ill patients. Nutrition 2018; 55-56:7–14 - PubMed
-
- Cirstea M, Walley KR, Russell JA, et al. : Decreased high-density lipoprotein cholesterol level is an early prognostic marker for organ dysfunction and death in patients with suspected sepsis. J Crit Care 2017; 38:289–294 - PubMed
Publication types
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

