Knockdown of NADPH oxidase 4 reduces mitochondrial oxidative stress and neuronal pyroptosis following intracerebral hemorrhage
- PMID: 36751799
- PMCID: PMC10154488
- DOI: 10.4103/1673-5374.360249
Knockdown of NADPH oxidase 4 reduces mitochondrial oxidative stress and neuronal pyroptosis following intracerebral hemorrhage
Abstract
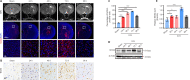
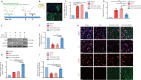
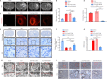
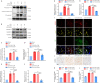
Intracerebral hemorrhage is often accompanied by oxidative stress induced by reactive oxygen species, which causes abnormal mitochondrial function and secondary reactive oxygen species generation. This creates a vicious cycle leading to reactive oxygen species accumulation, resulting in progression of the pathological process. Therefore, breaking the cycle to inhibit reactive oxygen species accumulation is critical for reducing neuronal death after intracerebral hemorrhage. Our previous study found that increased expression of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide phosphate oxidase 4 (NADPH oxidase 4, NOX4) led to neuronal apoptosis and damage to the blood-brain barrier after intracerebral hemorrhage. The purpose of this study was to investigate the role of NOX4 in the circle involving the neuronal tolerance to oxidative stress, mitochondrial reactive oxygen species and modes of neuronal death other than apoptosis after intracerebral hemorrhage. We found that NOX4 knockdown by adeno-associated virus (AAV-NOX4) in rats enhanced neuronal tolerance to oxidative stress, enabling them to better resist the oxidative stress caused by intracerebral hemorrhage. Knockdown of NOX4 also reduced the production of reactive oxygen species in the mitochondria, relieved mitochondrial damage, prevented secondary reactive oxygen species accumulation, reduced neuronal pyroptosis and contributed to relieving secondary brain injury after intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Finally, we used a mitochondria-targeted superoxide dismutase mimetic to explore the relationship between reactive oxygen species and NOX4. The mitochondria-targeted superoxide dismutase mimetic inhibited the expression of NOX4 and neuronal pyroptosis, which is similar to the effect of AAV-NOX4. This indicates that NOX4 is likely to be an important target for inhibiting mitochondrial reactive oxygen species production, and NOX4 inhibitors can be used to alleviate oxidative stress response induced by intracerebral hemorrhage.
Keywords: NADPH oxidase 4; caspase 1; caspase4/11; gasdermin D; intracerebral hemorrhage; mitochondria reactive oxygen species inhibitor; neuronal pyroptosis; neuronal tolerance; reactive oxygen species; secondary brain injury.
Conflict of interest statement
None
Figures

Similar articles
-
Inhibition of NOX4/ROS Suppresses Neuronal and Blood-Brain Barrier Injury by Attenuating Oxidative Stress After Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Front Cell Neurosci. 2020 Nov 13;14:578060. doi: 10.3389/fncel.2020.578060. eCollection 2020. Front Cell Neurosci. 2020. PMID: 33281556 Free PMC article.
-
Pharmacological inhibition of NOX4 ameliorates alcohol-induced liver injury in mice through improving oxidative stress and mitochondrial function.Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017 Jan;1861(1 Pt A):2912-2921. doi: 10.1016/j.bbagen.2016.09.009. Epub 2016 Sep 12. Biochim Biophys Acta Gen Subj. 2017. PMID: 27634671 Free PMC article.
-
The role of reactive oxygen species derived from different NADPH oxidase isoforms and mitochondria in oxalate-induced oxidative stress and cell injury.Urolithiasis. 2022 Apr;50(2):149-158. doi: 10.1007/s00240-022-01309-2. Epub 2022 Feb 6. Urolithiasis. 2022. PMID: 35128564 Free PMC article.
-
Implication of Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide Phosphate (NADPH) Oxidase and Its Inhibitors in Alzheimer's Disease Murine Models.Antioxidants (Basel). 2021 Feb 2;10(2):218. doi: 10.3390/antiox10020218. Antioxidants (Basel). 2021. PMID: 33540840 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Oxidative Stress Induced by Reactive Oxygen Species (ROS) and NADPH Oxidase 4 (NOX4) in the Pathogenesis of the Fibrotic Process in Systemic Sclerosis: A Promising Therapeutic Target.J Clin Med. 2021 Oct 19;10(20):4791. doi: 10.3390/jcm10204791. J Clin Med. 2021. PMID: 34682914 Free PMC article. Review.
Cited by
-
Research Progress on Effects of Ginsenoside Rg2 and Rh1 on Nervous System and Related Mechanisms.Molecules. 2023 Dec 4;28(23):7935. doi: 10.3390/molecules28237935. Molecules. 2023. PMID: 38067664 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Activating MC4R Promotes Functional Recovery by Repressing Oxidative Stress-Mediated AIM2 Activation Post-spinal Cord Injury.Mol Neurobiol. 2024 Aug;61(8):6101-6118. doi: 10.1007/s12035-024-03936-9. Epub 2024 Jan 26. Mol Neurobiol. 2024. PMID: 38277117
-
Dual-responsive nanoscale ultrasound contrast agent as an oxidative stress amplifier for enhanced DNA damage in BRCA-proficient ovarian cancer.Mater Today Bio. 2025 Apr 11;32:101761. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2025.101761. eCollection 2025 Jun. Mater Today Bio. 2025. PMID: 40270892 Free PMC article.
-
Mitochondrial Quality Control: Insights into Intracerebral Hemorrhage.Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025 Aug 14;45(1):79. doi: 10.1007/s10571-025-01599-1. Cell Mol Neurobiol. 2025. PMID: 40810912 Free PMC article. Review.
-
NADPH oxidase 4 (NOX4) as a biomarker and therapeutic target in neurodegenerative diseases.Neural Regen Res. 2024 Sep 1;19(9):1961-1966. doi: 10.4103/1673-5374.390973. Epub 2023 Dec 15. Neural Regen Res. 2024. PMID: 38227522 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Bao Q, Hu P, Xu Y, Cheng T, Wei C, Pan L, Shi J. Simultaneous blood-brain barrier crossing and protection for stroke treatment based on edaravone-loaded ceria nanoparticles. ACS Nano. (2018);12:6794–6805. - PubMed
-
- Brown GC, Borutaite V. There is no evidence that mitochondria are the main source of reactive oxygen species in mammalian cells. Mitochondrion. (2012);12:1–4. - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

