Hepatocytes demarcated by EphB2 contribute to the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
- PMID: 36753562
- PMCID: PMC10234568
- DOI: 10.1126/scitranslmed.adc9653
Hepatocytes demarcated by EphB2 contribute to the progression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis
Abstract
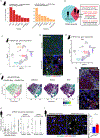
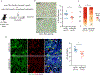
Current therapeutic strategies for treating nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) have failed to alleviate liver fibrosis, which is a devastating feature leading to hepatic dysfunction. Here, we integrated single-nucleus transcriptomics and epigenomics to characterize all major liver cell types during NASH development in mice and humans. The bifurcation of hepatocyte trajectory with NASH progression was conserved between mice and humans. At the nonalcoholic fatty liver (NAFL) stage, hepatocytes exhibited metabolic adaptation, whereas at the NASH stage, a subset of hepatocytes was enriched for the signatures of cell adhesion and migration, which were mainly demarcated by receptor tyrosine kinase ephrin type B receptor 2 (EphB2). EphB2, acting as a downstream effector of Notch signaling in hepatocytes, was sufficient to induce cell-autonomous inflammation. Knockdown of Ephb2 in hepatocytes ameliorated inflammation and fibrosis in a mouse model of NASH. Thus, EphB2-expressing hepatocytes contribute to NASH progression and may serve as a potential therapeutic target.
Conflict of interest statement
Competing interests:
M.A.L. is an advisory board member and has received research support from Pfizer Inc. He is also a scientific co-founder and advisory board member of Flare Therapeutics, and consultant to Madrigal Pharmaceuticals. The remaining authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Figures




References
-
- Golabi P, Paik JM, AlQahtani S, Younossi Y, Tuncer G, Younossi ZM, Burden of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease in Asia, the Middle East and North Africa: Data from Global Burden of Disease 2009–2019. J Hepatol 75, 795–809 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Albhaisi SAM, Sanyal AJ, New drugs for NASH. Liver Int 41 Suppl 1, 112–118 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Vuppalanchi R, Noureddin M, Alkhouri N, Sanyal AJ, Therapeutic pipeline in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol 18, 373–392 (2021). - PubMed
-
- Sanyal AJ, Anstee QM, Trauner M, Lawitz EJ, Abdelmalek MF, Ding D, Han L, Jia C, Huss RS, Chung C, Wong VW, Okanoue T, Romero-Gomez M, Muir AJ, Afdhal NH, Bosch J, Goodman Z, Harrison SA, Younossi ZM, Myers RP, Cirrhosis Regression is Associated with Improved Clinical Outcomes in Patients with Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology, (2021). - PMC - PubMed
-
- Deczkowska A, David E, Ramadori P, Pfister D, Safran M, At The B, Giladi A, Jaitin DA, Barboy O, Cohen M, Yofe I, Gur C, Shlomi-Loubaton S, Henri S, Suhail Y, Qiu M, Kam S, Hermon H, Lahat E, Ben Yakov G, Cohen-Ezra O, Davidov Y, Likhter M, Goitein D, Roth S, Weber A, Malissen B, Weiner A, Ben-Ari Z, Heikenwälder M, Elinav E, Amit I, XCR1(+) type 1 conventional dendritic cells drive liver pathology in non-alcoholic steatohepatitis. Nat Med 27, 1043–1054 (2021). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

