Targeted Dephosphorylation of Tau by Phosphorylation Targeting Chimeras (PhosTACs) as a Therapeutic Modality
- PMID: 36753634
- PMCID: PMC11670127
- DOI: 10.1021/jacs.2c11706
Targeted Dephosphorylation of Tau by Phosphorylation Targeting Chimeras (PhosTACs) as a Therapeutic Modality
Abstract
Microtubule-associated protein tau is essential for microtubule assembly and stabilization. Hyperphosphorylation of the microtubule-associated protein tau plays an important pathological role in the development of Alzheimer's disease and other tauopathies. In vivo studies using kinase inhibitors suggest that reducing tau phosphorylation levels has therapeutic potential; however, such approaches showed limited benefits. We sought to further develop our phosphorylation targeting chimera (PhosTAC) technology to specifically induce tau dephosphorylation. Herein, we use small molecule-based PhosTACs to recruit tau to PP2A, a native tau phosphatase. PhosTACs induced the formation of a stable ternary complex, leading to rapid, efficient, and sustained tau dephosphorylation, which also correlated with the enhanced downregulation of tau protein. Mass spectrometry data validated that PhosTACs downregulated multiple phosphorylation sites of tau. We believe that PhosTAC possesses several advantages over current strategies to modulate tau phosphorylation and represents a new avenue for disease-modifying therapies for tauopathies.
Conflict of interest statement
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no competing financial interest.
Figures
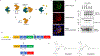
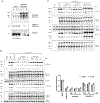
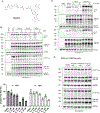
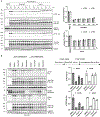
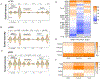
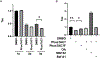
References
-
- Lee G; Cowan N; Kirschner M The primary structure and heterogeneity of tau protein from mouse brain. Science 1988, 239 (4837), 285–8. - PubMed
-
- Alzheimer A; Stelzmann RA; Schnitzlein HN; Murtagh FR An English translation of Alzheimer’s 1907 paper, “Uber eine eigenartige Erkankung der Hirnrinde”. Clin Anat 1995, 8 (6), 429–31. - PubMed
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

