Morbid obesity's impact on COVID-19 patients requiring venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: The covid-19 critical care consortium database review
- PMID: 36753684
- PMCID: PMC9912044
- DOI: 10.1177/02676591231156487
Morbid obesity's impact on COVID-19 patients requiring venovenous extracorporeal membrane oxygenation: The covid-19 critical care consortium database review
Abstract
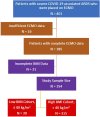
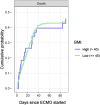
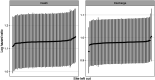
Introduction: Obesity is associated with a worse prognosis in COVID-19 patients with acute respiratory distress syndrome (ARDS). Veno-venous (V-V) Extracorporeal Membrane Oxygenation (ECMO) can be a rescue option, however, the direct impact of morbid obesity in this select group of patients remains unclear.Methods: This is an observational study of critically ill adults with COVID-19 and ARDS supported by V-V ECMO. Data are from 82 institutions participating in the COVID-19 Critical Care Consortium international registry. Patients were admitted between 12 January 2020 to 27 April 2021. They were stratified based on Body Mass Index (BMI) at 40 kg/m2. The endpoint was survival to hospital discharge.Results: Complete data available on 354 of 401 patients supported on V-V ECMO. The characteristics of the high BMI (>40 kg/m2) and lower BMI (≤40 kg/m2) groups were statistically similar. However, the 'high BMI' group were comparatively younger and had a lower APACHE II score. Using survival analysis, older age (Hazard Ratio, HR 1.49 per-10-years, CI 1.25-1.79) and higher BMI (HR 1.15 per-5 kg/m2 increase, CI 1.03-1.28) were associated with a decreased patient survival. A safe BMI threshold above which V-V ECMO would be prohibitive was not apparent and instead, the risk of an adverse outcome increased linearly with BMI.Conclusion: In COVID-19 patients with severe ARDS who require V-V ECMO, there is an increased risk of death associated with age and BMI. The risk is linear and there is no BMI threshold beyond which the risk for death greatly increases.
Keywords: COVID-19; acute respiratory distress syndrome; extracorporeal membrane oxygenation; morbid obesity.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of conflicting interestsThe author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Figures


References
-
- Combes A, Hajage D, Capellier G, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe acute respiratory distress syndrome. N Engl J Med 2018; 378: 1965–1975. - PubMed
-
- Peek GJ, Mugford M, Tiruvoipati R, et al. Efficacy and economic assessment of conventional ventilatory support versus extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for severe adult respiratory failure (CESAR): a multicentre randomised controlled trial. Lancet 2009; 374: 1351–1363. - PubMed
-
- Davies A, Jones D, Bailey M, et al. Extracorporeal membrane oxygenation for 2009 Influenza A (H1N1) acute respiratory distress syndrome. JAMA 2009; 302: 1888–1895. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

