Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease on Outcomes of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
- PMID: 36753753
- PMCID: PMC9969770
- DOI: 10.14503/THIJ-22-7873
Impact of Chronic Kidney Disease on Outcomes of Percutaneous Coronary Intervention in Patients With Diabetes Mellitus: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis
Abstract
Background: The impact of chronic kidney disease (CKD) on adverse cardiovascular outcomes after percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with diabetes mellitus (DM) is still unclear. This study aimed to systematically assess evidence on this topic.
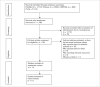
Methods: The PubMed, Embase, and CENTRAL databases were searched for studies comparing mortality, myocardial infarction (MI), or revascularization outcomes between patients with DM with and without CKD.
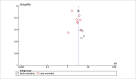
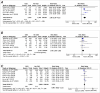
Results: In 11 studies, the presence of CKD was associated with significantly increased risk of early all-cause mortality (risk ratio [RR], 3.45; 95% CI, 3.07-3.87; I2 = 0%; P < .001), late all-cause mortality (RR, 2.78; 95% CI, 1.92-4.02; I2 = 83%; P < .001), cardiac mortality (RR, 2.90; 95% CI, 1.99-4.22; I2 = 29%; P < .001), and MI (RR, 1.40; 95% CI, 1.06-1.85; I2 = 13%; P = .02) compared with no CKD. There was no difference in the risk of any revascularization between those with and without CKD. Analysis of adjusted hazard ratios (HRs) indicated significantly increased risk of mortality (HR, 2.64; 95% CI, 1.91-3.64; I2 = 0%; P < .001) in the CKD group but only a nonsignificant tendency of increased MI (HR, 1.59; 95% CI, 0.99-2.54; I2 = 0%; P = .05) and revascularization (HR, 1.24; 95% CI, 0.94-1.63; I2 = 2%; P = .12) in the CKD group.
Conclusion: The presence of CKD in patients with DM significantly increases the risk of mortality and MI. However, CKD had no impact on revascularization rates.
Keywords: Renal failure; coronary artery disease; diabetes mellitus; kidney disease; mortality.
© 2023 by the Texas Heart® Institute, Houston.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Lin MJ, Chang YJ, Chen CY, Huang CC, Chuang TY, Wu HP. Influence of hypercholesterolemia and diabetes on long-term outcome in patients with stable coronary artery disease receiving percutaneous coronary intervention. Medicine (Baltimore) . 2019;98(34):e16927. doi: 10.1097/MD.0000000000016927. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Zhu Y, Meng S, Chen M et al. Long-term prognosis of chronic total occlusion treated by successful percutaneous coronary intervention in patients with or without diabetes mellitus: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Cardiovasc Diabetol . 2021;20(1):29. doi: 10.1186/s12933-021-01223-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical

