Effects of Octreotide-Long-Acting Release Added-on Tolvaptan in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Pilot, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Cross-Over Trial
- PMID: 36754009
- PMCID: PMC10103320
- DOI: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000049
Effects of Octreotide-Long-Acting Release Added-on Tolvaptan in Patients with Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: Pilot, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled, Cross-Over Trial
Abstract
Background: Tolvaptan and octreotide-long-acting release (LAR) have renoprotective effects in autosomal dominant polycystic kidney disease (ADPKD) that are partially mediated by amelioration of compensatory glomerular hyperfiltration. We compared the effects of tolvaptan and octreotide-LAR combination therapy versus those of tolvaptan monotherapy in patients with ADPKD.
Methods: This pilot, randomized, placebo-controlled, cross-over trial primarily compared the effects of 1- and 4-week treatments with octreotide-LAR (two 20-mg i.m. injections) or placebo (two i.m. 0.9% saline solution injections) added-on tolvaptan (up to 90 and 30 mg/d) on GFR (iohexol plasma clearance) in 19 consenting patients with ADPKD referred to a clinical research center in Italy. Analyses were intention-to-treat. The local ethical committee approved the study.
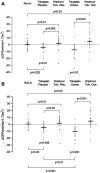
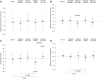
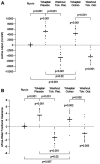
Results: At 4 weeks, GFR significantly decreased by a median (interquartile range) of 3 (-1 to 5) ml/min per 1.73 m2 with tolvaptan and placebo (P=0.01) and by 7 (3-14) ml/min per 1.73 m2 with tolvaptan and octreotide-LAR (P=0.03). GFR changes during the two treatment periods differed by 2 (-5 to 14) ml/min per 1.73 m2 (P=0.28). At 1 week, GFR significantly decreased by 3 (0-7) ml/min per 1.73 m2 with tolvaptan and placebo (P=0.006) and by 10 (-6 to 16) ml/min per 1.73 m2 with tolvaptan and octreotide-LAR add-on therapy (P<0.001). GFR changes during the two treatment periods significantly differed by 3 (0-12) ml/min per 1.73 m2 (P=0.012). Total kidney volume nonsignificantly changed by 4 (-48 to 23) ml with tolvaptan and placebo (P=0.74), whereas it decreased significantly by 41 (25-77) ml with tolvaptan and octreotide-LAR (P=0.001). Changes during the two treatment periods differed by 36 (0-65) ml (P=0.01). Octreotide-LAR also attenuated (P=0.02) the aquaretic effect of tolvaptan. Treatments were well tolerated.
Conclusions: In patients with ADPKD, octreotide-LAR added-on tolvaptan reduced GFR more effectively than octreotide-LAR and placebo. Octreotide-LAR also reduced total and cystic kidney volumes and attenuated the acquaretic effect of tolvaptan.
Clinical trial registry name and registration number: Tolvaptan-Octreotide LAR Combination in ADPKD (TOOL), NCT03541447.
Copyright © 2023 by the American Society of Nephrology.
Conflict of interest statement
A. Caroli reports research funding from Alexion Pharmaceuticals, Brembo, and Laminate Medical Technologies and speakers bureau for Fresenius Medical Care. F. Carrara, D. Cugini, D. Martinetti, T. Peracchi, A. Perna, N. Rubis, M. Trillini, and G. Villa report employment with Istituto di Ricerche Farmacologiche Mario Negri IRCCS. P. Ruggenenti and M. Caruso report employment with ASST Papa Giovanni XXIII. V.F. Leone reports employment with ASST Papa Giovanni XXIII; research funding from Achillion Pharmaceuticals, Alexion Pharmaceuticals, and Novartis Pharmaceutical company; and other interests or relationships with ERK Net. N. Perico reports research funding from Bayer AG and honoraria from Bayer S.p.A. G. Remuzzi reports consulting fees from Akebia Pharmaceuticals, Alexion Pharmaceutical, AstraZeneca, BioCryst Pharmaceuticals, Janssen Research & Development, Menarini Ricerche Spa, Otsuka, and Silence Therapeutics and serving as a member of numerous editorial boards of scientific medical journals. All remaining authors have nothing to disclose.
Figures


Comment in
-
Concurrent Targeting of Vasopressin Receptor 2 and Somatostatin Receptors in Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease: A Promising Approach for Autosomal Dominant Polycystic Kidney Disease Treatment?Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023 Feb 1;18(2):154-156. doi: 10.2215/CJN.0000000000000055. Epub 2023 Jan 16. Clin J Am Soc Nephrol. 2023. PMID: 36754002 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

