Preference of Escaped Mice for Live Capture or Glue Traps and Relevance to Pest Control Programs
- PMID: 36755208
- PMCID: PMC9936854
- DOI: 10.30802/AALAS-JAALAS-22-000073
Preference of Escaped Mice for Live Capture or Glue Traps and Relevance to Pest Control Programs
Abstract
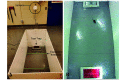
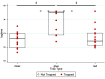
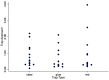
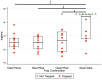
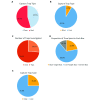
Insects are potential disease vectors for research animals. Therefore, implementing an effective pest control program is an essential component of any animal care and use program. The Guide for the Care and Use of Laboratory Animals emphasizes the humane use of traps; however, insect traps commonly use glue that can entrap escaped research mice, leading to their potential distress and injury. This situation is challenging for research facilities attempting to identify insect populations. In an effort to improve pest control in animal facilities, we sought to characterize the behavioral interactions of mice with common vermin traps. Three experiments using different combinations of traps (glue trap, live mouse trap with a clear viewing window, and live mouse trap with a red-tinted viewing window) were used in multiple behavioral testing arenas to address these questions. Experiments 1 and 2 were performed in a small arena, and Experiment 3 was performed in a simulated mouse housing room. Dependent measures included exploration of the test environment, grooming behavior, time spent near each trap, and latency to capture. Results indicate that mice were captured significantly more quickly by live traps than by glue traps, and were far more likely to enter a live trap as compared with a glue trap. Mice did not appear to differentiate between clear or red-tinted window live traps. Taken together, the results indicate that deploying both a live trap and a glue trap will allow humane capture of escaped mice yet will also capture insects in the same environment.
Figures


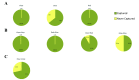
References
-
- AAALAC International. [Internet]. 2022. Frequency of Monitoring Rodent Traps. FAQs. [Cited 24 June 2022]. Available at: https://www.aaalac.org/accreditation-program/faqs/#C
-
- Clancy BM, Theriault BR, Schoenberger JM, Bowers CJ, Mitchell CM, Langan GP, Ostdiek AM, Luchins KR. 2022. Identification and control of an Ornithonyssus bacoti infestation in a rodent vivarium by using molecular diagnostic techniques. Comp Med 72:113–121. 10.30802/AALAS-CM-21-000105. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Corrigan RM. 1998. The efficacy of glue traps against wild populations of house mice, Mus domesticus Rutty. In Proceedings of the Vertebrate Pest Conference 18: 268–275. 10.5070/V418110049 - DOI
Publication types
MeSH terms
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

