Competing endogenous RNA network analysis of the molecular mechanisms of ischemic stroke
- PMID: 36755220
- PMCID: PMC9906963
- DOI: 10.1186/s12864-023-09163-1
Competing endogenous RNA network analysis of the molecular mechanisms of ischemic stroke
Abstract
Background: Ischemic stroke (IS) is a serious neurological disease that largely results in long-term disability and death. Extensive evidence has indicated that the activation of inflammation and ferroptosis significantly contribute to the development of IS pathology. However, the underlying molecular mechanism remains unclear. In this study, we aimed to identify potential biomarkers associated with IS through the construction of a competing endogenous RNA (ceRNA) network and to investigate the possible inflammatory and ferroptosis-related molecular mechanisms.
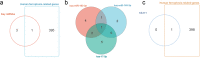
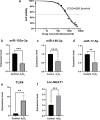
Results: We identified 178 differentially expressed target messenger RNAs (DETmRNAs) associated with IS. As revealed through enrichment analysis, the DEmRNAs were mainly enriched in the inflammatory signaling pathways and also related to ferroptosis mechanism. The CIBERSORT algorithm showed immune infiltration landscapes in which the naïve B cells, naïve T cells, and monocytes had statistically different numbers in the cerebral infarction group compared with the control group. A ceRNA network was constructed in this study involving 44 long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), 15 microRNAs (miRNAs), and 160 messenger RNAs (mRNAs). We used the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) analysis to identify three miRNAs (miR-103a-3p, miR-140-3p, and miR-17-5p), one mRNA (TLR4), and one lncRNA (NEAT1) as the potential key biomarkers of the ceRNA network. The key mRNA and lncRNA were shown to be highly related to the ferroptosis mechanism of IS. The expression of these key biomarkers was also further validated by a method of quantitative real-time polymerase chain reaction in SH-SY5Y cells, and the validated results were consistent with the findings predicted by bioinformatics.
Conclusion: Our results suggest that the ceRNA network may exert an important role in the inflammatory and ferroptosis molecular mechanisms of IS, providing new insight into therapeutic IS targets.
Keywords: Biomarker; Ferroptosis; Inflammatory response; Ischemic stroke; Network analysis.
© 2023. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures








References
-
- Pu L, Wang M, Li K, et al. Identification micro-RNAs functional modules and genes of ischemic stroke based on weighted gene co-expression network analysis (WGCNA)[J] Genomics. 2020;112(4):2748–2754. - PubMed
-
- Ding Q, Liu S, Yao Y, et al. Global, regional, and National Burden of ischemic stroke, 1990-2019[J] Neurology. 2022;98(3):e279–e290. - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Research Materials

