Cuproptosis-related gene FDX1 as a prognostic biomarker for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma correlates with immune checkpoints and immune cell infiltration
- PMID: 36755576
- PMCID: PMC9900009
- DOI: 10.3389/fgene.2023.1071694
Cuproptosis-related gene FDX1 as a prognostic biomarker for kidney renal clear cell carcinoma correlates with immune checkpoints and immune cell infiltration
Abstract
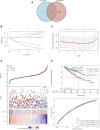
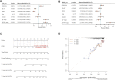
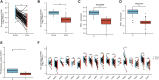
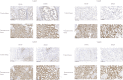
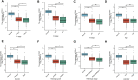
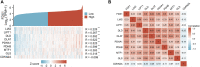
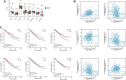
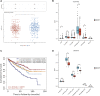
Background: Kidney renal clear cell carcinoma (KIRC) is not sensitive to radiotherapy and chemotherapy, and only some KIRC patients can benefit from immunotherapy and targeted therapy. Cuproptosis is a new mechanism of cell death, which is closely related to tumor progression, prognosis and immunity. The identification of prognostic markers related to cuproptosis in KIRC may provide targets for treatment and improve the prognosis of KIRC patients. Methods: Ten cuproptosis-related genes were analyzed for differential expression in KIRC-TCGA and a prognostic model was constructed. Nomogram diagnostic model was used to screen independent prognostic molecules. The screened molecules were verified in multiple datasets (GSE36895 and GSE53757), and in KIRC tumor tissues by RT-PCR and immunohistochemistry (IHC). Clinical correlation of cuproptosis-related independent prognostic molecules was analyzed. According to the molecular expression, the two groups were divided into high and low expression groups, and the differences of immune checkpoint and tumor infiltrating lymphocytes (TILs) between the two groups were compared by EPIC algorithm. The potential Immune checkpoint blocking (ICB) response of high and low expression groups was predicted by the "TIDE" algorithm. Results: FDX1 and DLAT were protective factors, while CDKN2A was a risk factor. FDX1 was an independent prognostic molecule by Nomogram, and low expressed in tumor tissues compared with adjacent tissues (p < 0.05). FDX1 was positively correlated with CD274, HAVCR2, PDCD1LG2, and negatively correlated with CTLA4, LAG3, and PDCD1. The TIDE score of low-FDX1 group was higher than that of high-FDX1 group. The abundance of CD4+ T cells, CD8+ T cells and Endothelial cells in FDX1-low group was lower than that in FDX1-high group (p < 0.05). Conclusion: FDX1, as a key cuproptosis-related gene, was also an independent prognostic molecule of KIRC. FDX1 might become an interesting biomarker and potential therapeutic target for KIRC.
Keywords: cuproptosis-related gene; fdx1; immune cell infiltration; immune checkpoints; kidney renal clear cell carcinoma; prognostic biomarker.
Copyright © 2023 Yao, Chen, Lou and Chen.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alsaab H. O., Sau S., Alzhrani R. M., Cheriyan V. T., Polin L. A., Vaishampayan U., et al. (2018). Tumor hypoxia directed multimodal nanotherapy for overcoming drug resistance in renal cell carcinoma and reprogramming macrophages. Biomaterials 183, 280–294. 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2018.08.053 - DOI - PMC - PubMed
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

