Updates on Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Renal Anemia
- PMID: 36756084
- PMCID: PMC9900466
- DOI: 10.1159/000527835
Updates on Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Renal Anemia
Abstract
Background: Anemia is a common complication of chronic kidney disease. The hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor (HIF-PHI) is a new class of oral drugs for the treatment of renal anemia.
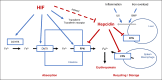
Summary: Clinical trials have consistently shown that HIF-PHIs can effectively increase hemoglobin in both the dialysis population and the nondialysis population. The effects of HIF-PHIs in treating renal anemia include promoting endogenous erythropoietin production and facilitating iron mobilization. Several studies suggest that the erythropoiesis effect of roxadustat is less affected by inflammation. Careful monitoring of thromboembolic events and tumor before and during HIF-PHI treatment is necessary.
Key messages: HIF-PHIs are effective in correcting renal anemia. The long-term safety of HIF-PHIs needs to be further studied.
Keywords: Anemia; Chronic kidney disease; Hypoxia-inducible factor; Iron.
Copyright © 2022 by The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Chuan-Ming Hao received honoraria from FibroGen for speaking engagements and advisory board participation related to physician education. The other authors do not disclose any conflicts of interest. Volker H. Haase is a scientific advisor and has received honoraria from Akebia Therapeutics. Volker H. Haase is supported by the Krick-Brooks Chair in Nephrology.
Figures

Similar articles
-
Future perspectives of anemia management in chronic kidney disease using hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors.Pharmacol Ther. 2022 Nov;239:108272. doi: 10.1016/j.pharmthera.2022.108272. Epub 2022 Aug 27. Pharmacol Ther. 2022. PMID: 36031160 Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors for renal anemia in chronic kidney disease: Advantages and disadvantages.Eur J Pharmacol. 2021 Dec 5;912:174583. doi: 10.1016/j.ejphar.2021.174583. Epub 2021 Oct 19. Eur J Pharmacol. 2021. PMID: 34678238 Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor-prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in the treatment of anemia of chronic kidney disease.Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2021 Apr;11(1):8-25. doi: 10.1016/j.kisu.2020.12.002. Epub 2021 Mar 18. Kidney Int Suppl (2011). 2021. PMID: 33777492 Free PMC article.
-
Safety and Efficacy of Hypoxia-Inducible Factor-Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors vs. Erythropoietin-Stimulating Agents in Treating Anemia in Renal Patients (With or Without Dialysis): A Meta-Analysis and Systematic Review.Cureus. 2023 Oct 21;15(10):e47430. doi: 10.7759/cureus.47430. eCollection 2023 Oct. Cureus. 2023. PMID: 38021836 Free PMC article. Review.
-
Hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor in the treatment of anemia in chronic kidney disease.Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2020 Jul;29(4):414-422. doi: 10.1097/MNH.0000000000000617. Curr Opin Nephrol Hypertens. 2020. PMID: 32452915 Review.
Cited by
-
Platelets in Renal Disease.Int J Mol Sci. 2023 Sep 29;24(19):14724. doi: 10.3390/ijms241914724. Int J Mol Sci. 2023. PMID: 37834171 Free PMC article. Review.
-
WHOLE TRANSCRIPTION ANALYSIS IDENTIFIED THE REGULATION OF HYPOXIA-INDUCIBLE FACTORS IN MONOCYTES WITH IMMUNE SUPPRESSION: IMPLICATIONS FOR CLINICAL OUTCOMES.Shock. 2025 Apr 1;63(4):541-551. doi: 10.1097/SHK.0000000000002479. Epub 2024 Oct 2. Shock. 2025. PMID: 39405478 Free PMC article.
-
Efficacy and safety of hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitors in patients with chronic kidney disease: meta-analysis of phase 3 randomized controlled trials.Clin Kidney J. 2023 Jun 22;17(1):sfad143. doi: 10.1093/ckj/sfad143. eCollection 2024 Jan. Clin Kidney J. 2023. PMID: 38186871 Free PMC article.
-
Ischemic Stroke During Daprodustat Therapy for Renal Anemia: A Report of Three Cases.Cureus. 2024 Apr 10;16(4):e57990. doi: 10.7759/cureus.57990. eCollection 2024 Apr. Cureus. 2024. PMID: 38738133 Free PMC article.
-
Changes in Retinal Nerve Fiber Layer Thickness in Patients With Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis.Clin Respir J. 2025 Mar;19(3):e70065. doi: 10.1111/crj.70065. Clin Respir J. 2025. PMID: 40035189 Free PMC article.
References
-
- St Peter WL, Guo H, Kabadi S, Gilbertson DT, Peng Y, Pendergraft T. Prevalence, treatment patterns, and healthcare resource utilization in Medicare and commercially insured non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease patients with and without anemia in the United States. BMC Nephrol. 2018;19((1)):67. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoshino J, Muenz D, Zee J, Sukul N, Speyer E, Guedes M, et al. Associations of hemoglobin levels with health-related quality of life, physical activity, and clinical outcomes in persons with stage 3-5 nondialysis CKD. J Ren Nutr. 2020;30((5)):404–414. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

