Updates on Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Renal Anemia
- PMID: 36756084
- PMCID: PMC9900466
- DOI: 10.1159/000527835
Updates on Hypoxia-Inducible Factor Prolyl Hydroxylase Inhibitors in the Treatment of Renal Anemia
Abstract
Background: Anemia is a common complication of chronic kidney disease. The hypoxia-inducible factor prolyl hydroxylase inhibitor (HIF-PHI) is a new class of oral drugs for the treatment of renal anemia.
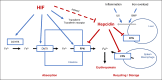
Summary: Clinical trials have consistently shown that HIF-PHIs can effectively increase hemoglobin in both the dialysis population and the nondialysis population. The effects of HIF-PHIs in treating renal anemia include promoting endogenous erythropoietin production and facilitating iron mobilization. Several studies suggest that the erythropoiesis effect of roxadustat is less affected by inflammation. Careful monitoring of thromboembolic events and tumor before and during HIF-PHI treatment is necessary.
Key messages: HIF-PHIs are effective in correcting renal anemia. The long-term safety of HIF-PHIs needs to be further studied.
Keywords: Anemia; Chronic kidney disease; Hypoxia-inducible factor; Iron.
Copyright © 2022 by The Author(s). Published by S. Karger AG, Basel.
Conflict of interest statement
Chuan-Ming Hao received honoraria from FibroGen for speaking engagements and advisory board participation related to physician education. The other authors do not disclose any conflicts of interest. Volker H. Haase is a scientific advisor and has received honoraria from Akebia Therapeutics. Volker H. Haase is supported by the Krick-Brooks Chair in Nephrology.
Figures

References
-
- St Peter WL, Guo H, Kabadi S, Gilbertson DT, Peng Y, Pendergraft T. Prevalence, treatment patterns, and healthcare resource utilization in Medicare and commercially insured non-dialysis-dependent chronic kidney disease patients with and without anemia in the United States. BMC Nephrol. 2018;19((1)):67. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Hoshino J, Muenz D, Zee J, Sukul N, Speyer E, Guedes M, et al. Associations of hemoglobin levels with health-related quality of life, physical activity, and clinical outcomes in persons with stage 3-5 nondialysis CKD. J Ren Nutr. 2020;30((5)):404–414. - PubMed
Publication types
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

